Backup strategy is a crucial component that every business must prioritize to ensure data protection and continuity in today’s digital landscape. A properly implemented backup strategy is crucial to an organization’s risk management. It helps safeguard valuable data from unexpected events such as hardware failures, unintentional deletions, or cybersecurity risks. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the basics of backup strategy, highlighting its importance and offering a guide on its implementation for businesses of all sizes.
What is a Backup Strategy?
A backup strategy is a crucial part of a company’s overall data protection plan. It involves creating and storing backup copies of critical data, which can be used to recover lost, deleted, or corrupted data in the event of a disaster or other unexpected incident. A well-designed strategy should consider several key factors, such as the types of backup to use, how frequently backups should be performed, the system and data store to be utilized, and the disaster recovery plan.
The types of backup a company chooses to use can vary depending on their specific needs and priorities. Full backups are a comprehensive backup of all data, while incremental and differential backups only backup changes made since the last backup. The backup frequency should be determined by how often the data changes and the importance of the data. Critical data should be backed up more frequently than less critical data.
The backup system and data store are also essential factors in a backup strategy. Companies may store backups on external hard drives, cloud storage, or network-attached storage (NAS). The copy should be kept in a secure location and, in some cases, offsite to provide additional protection against natural disasters, theft, or other unforeseen events.
Types of Backup
Data backup is a critical aspect of data management, and different types of backup strategies exist to help businesses protect their data. The most common types of backups include:
Full Backup
One of the most common types of backup is a full backup, which involves backing up all data and files stored on a device or system. This type of Backup creates a replica of the original data and is useful for restoring all data in case of a complete system failure.
However, performing full backups regularly can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Therefore, businesses should consider other backup strategies, such as incremental or differential backups.
These methods only back up the changes made since the last full backup and are more efficient regarding time and storage usage.
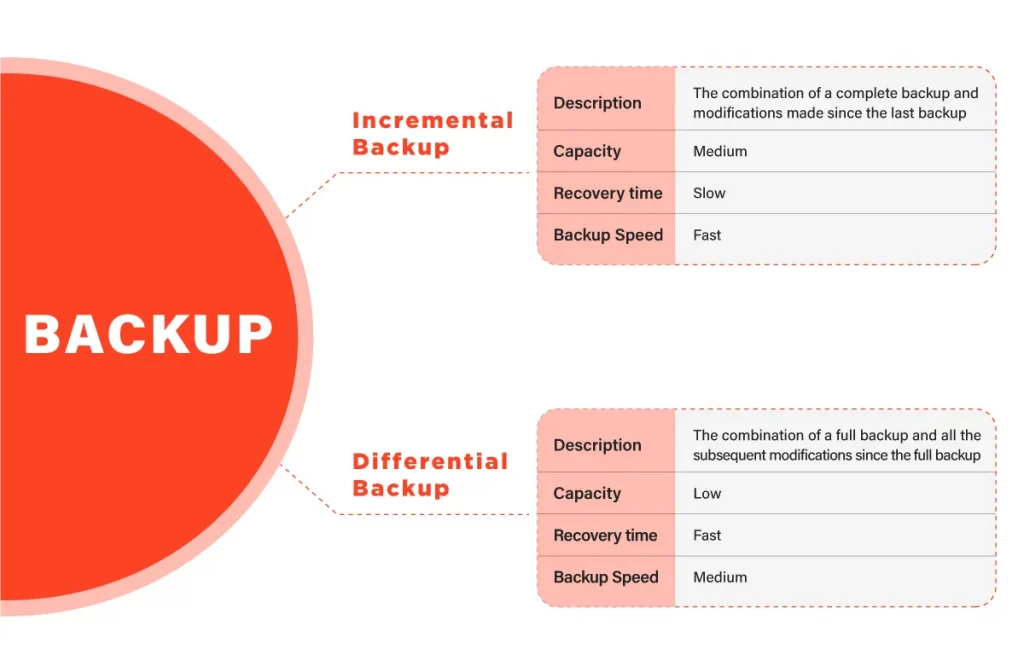
Incremental Backup
Another type of backup is an incremental backup, which only backs up data that has changed since the last copy. Incremental backups only note the changes made to files since the previous backup, which makes the process faster and less storage-intensive than full backups.
This type of backup is useful for businesses with a large volume of data that changes frequently, as it can be performed more often than a full backup without taking up too much storage space. However, restoring data from an incremental backup requires multiple steps and can be more time-consuming than a full backup.
Differential Backup
A differential backup is similar to an incremental backup in that it only backs up the changes made since the last full copy. However, unlike incremental backups, which only note changes since the last backup, differential backups record all changes made since the previous full backup.
This means that the size of a differential backup will continue to grow with each successive backup, making it less efficient than an incremental backup in terms of storage usage. However, restoring data from a differential backup is faster and requires fewer steps than an incremental backup.
The 3-2-1 Backup Strategy
The 3-2-1 backup strategy is a robust and popular backup method recommended for businesses of all sizes. This plan involves creating three backup copies of critical data, storing them in two different types of media, and keeping one copy offsite.
The three copies of data are the original data and two backup copies, while the two different kinds of media refer to two other devices or storage media that will be used to store the backups.
The primary advantage of the 3-2-1 strategy is its reliability and resilience. By keeping copies of data in two different media types, businesses can protect themselves against potential data loss resulting from hardware failure or system corruption. Keeping one copy of the backup offsite also provides extra protection against natural disasters.
Businesses can choose to store their backups in various media, including external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS), cloud storage, or tape drives. Each type of media has its advantages and disadvantages, and businesses should carefully consider which option is best for their specific needs.
The 3-2-1 backup strategy is flexible and scalable, allowing businesses to customize the backup frequency and storage options based on the volume and criticality of the data. It is also important to regularly test and verify the backups to ensure they can be restored in the event of data loss.
Backup System and Data Storage
Choosing the right backup system and data storage is crucial for any business to create a reliable and effective data backup strategy. Different strategies offer varying performance levels, scalability, and security, and companies must choose the option that best meets their specific needs.
Cloud storage is a data storage option that is becoming increasingly popular due to its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. These backup services allow businesses to store their data in a secure offsite location, which makes it easy to access and recover data in the event of data loss.

Cloud backup is also a good option for businesses with a lot of data to back up, as it provides virtually unlimited storage capacity and is scalable.
Network-attached storage (NAS) is a storage system attached to a network and can be accessed by multiple devices simultaneously. NAS systems are ideal for businesses that need to store large volumes of data and require high-speed access to their data.
They are used as backup devices, allowing companies to create a centralized system that can be accessed from multiple devices.
When selecting a backup system and data store, businesses must also consider the security and reliability of the system. Cloud backup providers typically offer high levels of security and reliability, but it is essential to choose a provider that meets your specific security and compliance requirements.
Data protection is a critical consideration for every business. Protecting sensitive business data is essential to ensure business continuity, maintain customer trust, and comply with regulatory requirements.
A solid backup and recovery plan is an essential component of data protection. It ensures that critical data is regularly backed up, and a copy is stored offsite to prevent loss due to natural disasters or cyber-attacks. Businesses should review and update their backup strategy regularly to ensure it meets their current needs. This includes considering the types of data being backed up, the frequency of backups, and the storage options available.
In addition to backups, businesses should consider implementing other actions to protect their data. This includes implementing security measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems. Employee training is also crucial, as human error remains a leading cause of data breaches. Training employees on proper data handling and security protocols can help prevent accidental data loss or theft.
Having a correct backup strategy is critical for businesses of all sizes. It ensures that important data and information are protected from loss or damage, whether due to human error, natural disasters, or cyber-attacks. A solid backup plan should include regular backups, secure storage, and quick restoration processes to minimize downtime in case of a disaster. By investing in a robust backup strategy, businesses can safeguard their most valuable assets and maintain continuity in their operations, thereby minimizing potential losses and ensuring the long-term success of their enterprise.
What is the 3-2-1 Backup Strategy?
The 3-2-1 backup strategy involves creating three copies of your data, storing them in two different media types, and keeping one copy offsite for disaster recovery.
What are some types of media for data backup?
Popular media for data backup include external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS), cloud storage, and tape drives.
Why should I use a cloud storage backup?
Cloud storage backups are scalable, flexible, and cost-effective. They allow for secure offsite storage, easy access, and data recovery, offering unlimited storage capacity.
What is a Disaster Recovery Plan?
A Disaster Recovery Plan is a documented process to recover and protect a business’s IT infrastructure during a disaster. It ensures that critical data is regularly backed up and a copy is stored offsite to prevent loss due to natural disasters or cyber-attacks.
Why is employee training crucial in data protection?
Human error remains a leading cause of data breaches. Training employees on proper data handling and security protocols can help prevent accidental data loss or theft.
