RAID 5 vs. RAID 6 is a common topic of discussion among tech enthusiasts and professionals seeking optimal data storage solutions. RAID is a method of storing the same data in a location placed on multiple hard disks to protect data during a drive failure.
While both RAID 5 and RAID 6 offer redundancy and reliability, they have distinct advantages and differences that make them suitable for different use cases. This blog post explores these two RAID configurations, highlighting their unique features, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
How RAID 5 Enhances Your Data Storage
RAID 5 is a type of RAID level that uses block-level striping with distributed parity. It requires a minimum of three drives to implement, with one drive dedicated to storing parity information. In RAID 5 arrays, data is divided into blocks and distributed evenly across all the drives in the array.
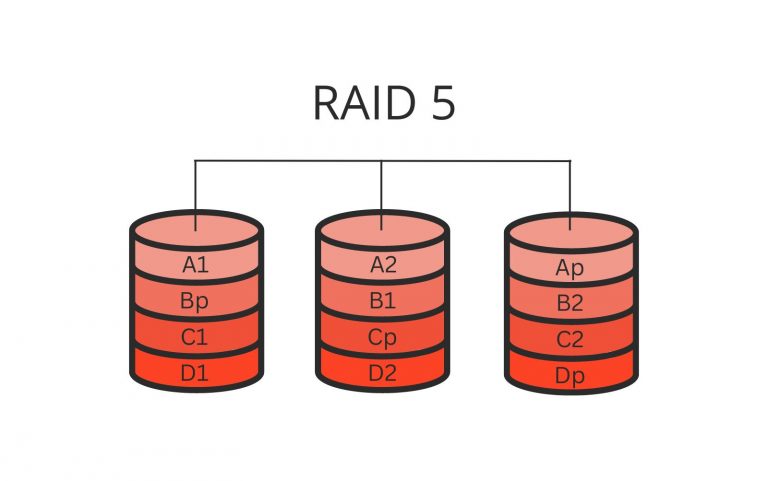
Parity information is also distributed across all the drives in the array. Hence, if any disks fail, the remaining ones can be used to reconstruct the lost data using the parity information.
RAID 6 Explained
RAID 6, a more advanced version of RAID 5, uses block-level striping with double-distributed parity. It requires a minimum of four hard drives to implement, with two drives dedicated to storing parity information. In RAID level 6, data is divided into blocks and distributed evenly across all the drives in the array, just like in RAID 5.
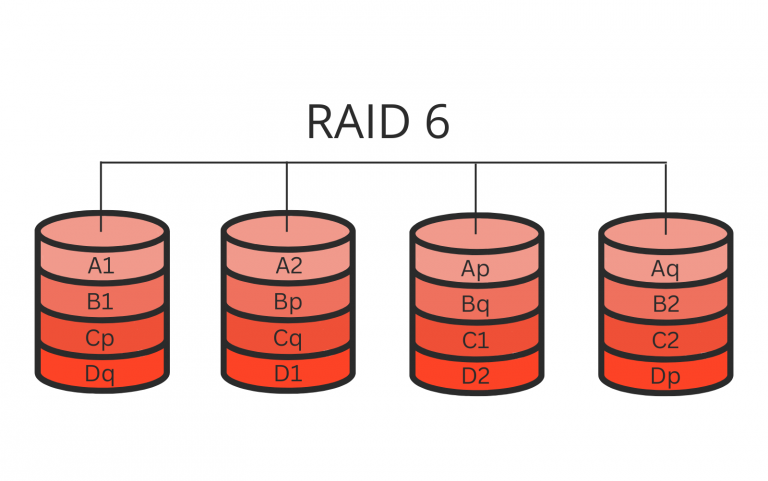
However, instead of one parity block, there are two parity blocks, each stored on a different drive. This means that even if two drives fail simultaneously, the array can reconstruct the lost data using the remaining drives and the parity information.
Main Differences - RAID 5 vs. RAID 6
Fault Tolerance
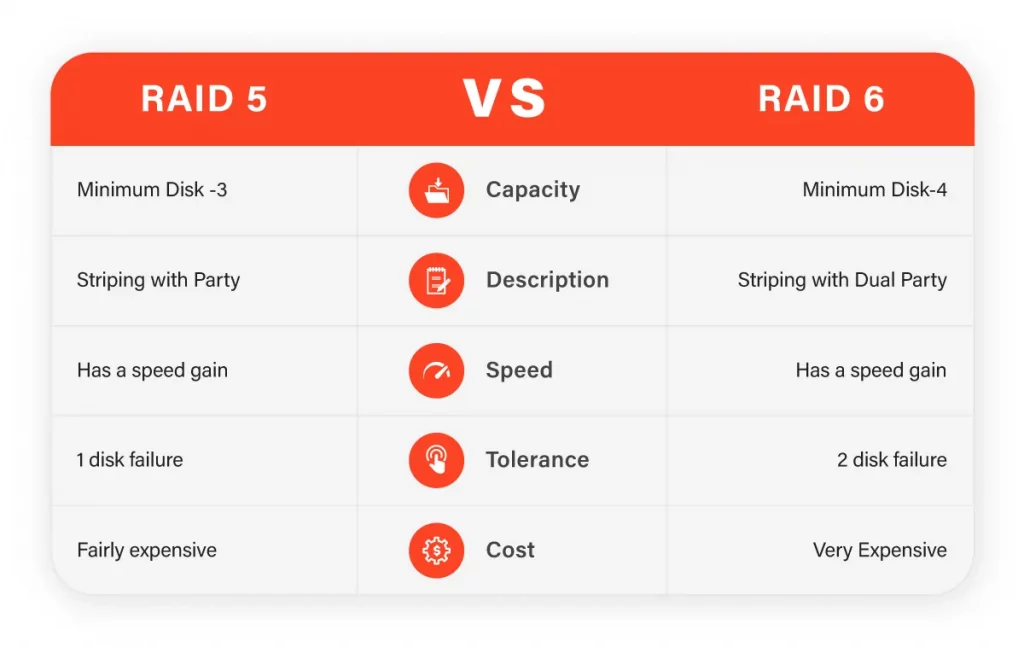
RAID 6 configuration is more fault-tolerant than RAID 5. RAID 5 can only withstand a single drive failure, while RAID 6 can withstand up to two simultaneously. This is because RAID 6 uses double-distributed parity, which means it can rebuild the lost data even if two drives fail. In contrast, RAID 5 can only rebuild data if a single drive fails.
Capacity and Performance
RAID 5 has a higher capacity and performance than RAID 6. This is because RAID 5 requires only one drive for parity information, while RAID 6 requires two drives for parity information. As a result, RAID 5 can store more data with the same number of drives and can access data faster than RAID 6. However, this difference in performance and capacity is only significant in large-scale storage systems with many hard drives.
Cost
RAID 5 is less expensive to implement than RAID 6. This is because RAID 5 requires fewer hard drives to implement, and each hard drive is cheaper than the hard drives used in RAID 6. Additionally, RAID 6 requires more advanced hardware and software to manage the additional parity information, which also increases the cost of implementation.
Use Cases
RAID 5 is suitable for general-purpose data storage and applications prioritizing performance over redundancy. It is commonly used in home computers, small businesses, and enterprise-level systems. On the other hand, RAID 6 is better suited for critical data storage and applications that require high redundancy and fault tolerance levels, such as financial systems and large-scale databases.
How to Choose Between RAID 5 vs. 6
Data Protection Requirements
If data protection is your top priority, RAID 6 is the better choice. RAID 6 can withstand up to two simultaneous drive failures, which means it offers more protection against data loss than RAID 5.
Performance and Storage Capacity
If you need high capacity and performance, RAID 5 may be the better choice. RAID 5 can store more data with the same number of drives and access data faster than RAID 6. However, this difference in performance and capacity is only significant in large-scale storage systems with many hard drives.
Cost
If cost is a significant factor, RAID 5 is the better choice. RAID 5 requires fewer hard drives to implement, and each hard drive is less expensive than the hard drives used in RAID 6. Additionally, RAID 6 requires more advanced hardware and software to manage the additional parity information, which also increases the cost of implementation.

Risk of Drive Failure
The risk of drive failure is essential when choosing between RAID 5 and RAID 6. If you have a large number of drives in your storage system, the risk of drive failure increases. RAID 6 is the better choice in such cases since it can withstand up to two simultaneous drive failures. However, if you have a small number of drives in your storage system, RAID 5 may be sufficient since the risk of drive failure is relatively low.
Type of Data
The data type you store is another factor to consider when choosing between RAID 5 and RAID 6. If you store critical data that needs to be accessed quickly, RAID 5 may be the better choice since it offers faster access times than RAID 6. However, if you store large amounts of data that do not require quick access times, RAID 6 may be the better choice since it offers better data protection.
Future Expansion
It is important to consider future expansion when choosing between RAID 5 and RAID 6. If you anticipate needing to add more drives to your storage system in the future, RAID 6 may be the better choice since it can withstand up to two simultaneous drive failures even with more drives added to the system.
In contrast, if you anticipate needing to add more drives to your storage system and are already using RAID 5, you may need to rebuild your entire storage system using RAID 6 to ensure adequate data protection.
RAID 5 and RAID 6 Data Recovery
In conclusion, the choice between RAID 5 and RAID 6 depends on your specific needs, with RAID 5 offering more storage capacity and higher performance, while RAID 6 provides enhanced fault tolerance. Regardless of the RAID configuration chosen, it’s important to remember that no system is completely immune to data loss.
At PITS Global Data Recovery Services, we offer exceptional RAID recovery services, helping businesses and individuals recover their valuable data with speed and accuracy. Don’t risk losing your vital information – Contact us today for secure and trusted RAID recovery solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between RAID 5 and RAID 6?
The primary difference lies in their fault tolerance capability. RAID 5 can resist a single drive failure, while RAID 6 can endure up to two simultaneous drive failures.
Which RAID type is more cost-effective?
RAID 5 is generally more cost-effective to implement than RAID 6, as it requires fewer hard drives and less advanced hardware.
Is RAID 5 or RAID 6 faster?
RAID 5 tends to provide faster data access than RAID 6 due to requiring only one drive for parity information.
Which RAID configuration is more suitable for critical data storage?
RAID 6 is preferred for critical data storage as it offers higher redundancy and fault tolerance levels, ideal for financial systems and large-scale databases.
Can RAID 5 and RAID 6 prevent all data loss?
While both RAID configurations improve data protection, no system is completely immune to data loss. It is recommended to have a secure data recovery plan in place.
