In the ever-evolving landscape of data storage and protection, RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and accessibility of data. Among the many RAID levels available, RAID 50 and RAID 60 stand out as two popular choices for organizations seeking a balance between performance and data protection. In this comprehensive comparison, we will delve into the intricacies of RAID 50 and RAID 60, exploring their differences in terms of parity calculations, number of disks, data loss prevention, drive failures, read and write operations, and more.
Understanding the Basics: RAID and Data Striping
Before we jump into the RAID 50 vs RAID 60 showdown, let’s quickly revisit the fundamental concept of RAID and data striping.
RAID arrays are formed by combining multiple hard drives into a single unit, offering various levels of redundancy and performance improvements. Data striping is a technique used in RAID to spread data across multiple drives, enhancing read and write speeds by breaking data into smaller segments, or “stripes.”
RAID 50: The Hybrid Performer
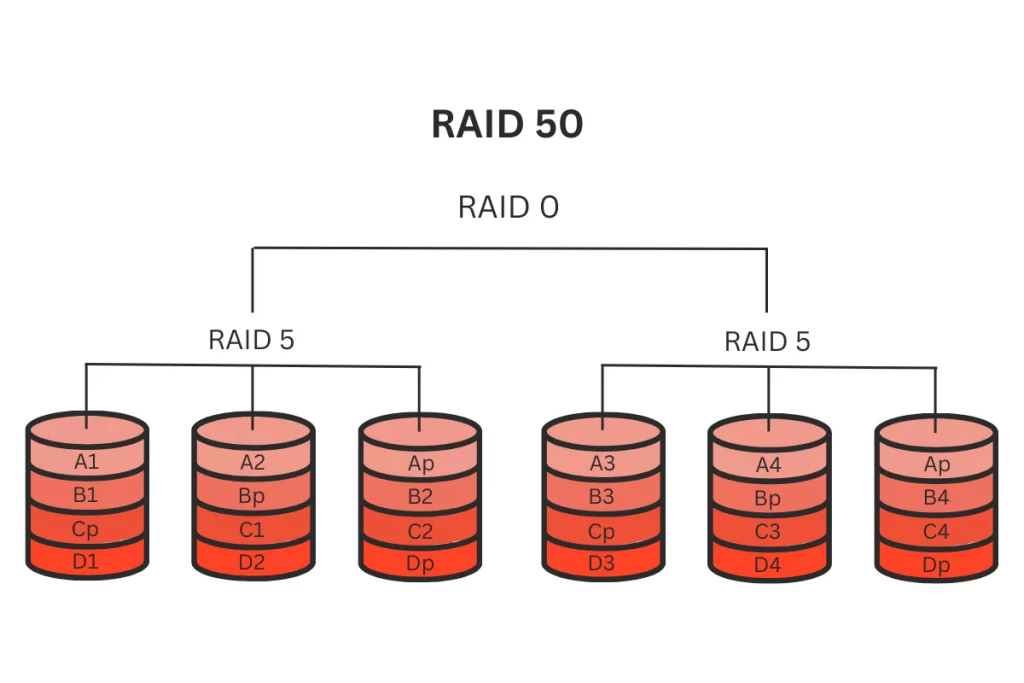
RAID 50 is a hybrid RAID level that combines the features of RAID 5 and RAID 0 arrays. In RAID 50, data striping is combined with distributed parity calculations. Here’s what sets RAID 50 apart:
- Number of Disks: RAID 50 requires a minimum of six drives to operate effectively. These drives are organized into multiple sets of parity data, with each set consisting of at least three drives.
- Data Protection: RAID 50 offers robust data protection through distributed parity. This means that if a single drive fails within a set of parity data, data can still be reconstructed from the remaining drives.
- Write Speed: Thanks to data striping, RAID 50 arrays exhibit excellent write speeds, making them suitable for applications with heavy write workloads.
- Drive Failure Tolerance: RAID 50 can tolerate the failure of a single drive within each set of parity data. However, if multiple drives within the same set fail simultaneously, data loss can occur.
- Similar to RAID 5: RAID 50 is often considered similar to RAID 5, as both levels use distributed parity for data protection. However, RAID 50 takes performance a step further with data striping.
RAID 60: Double the Safety
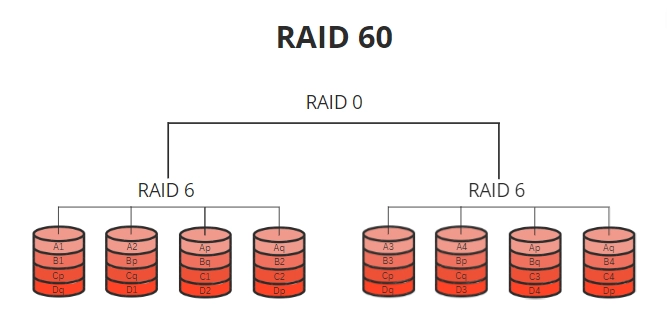
RAID 60, on the other hand, is a dual-parity RAID level that provides enhanced data protection compared to RAID 50. Here are its key characteristics:
- Number of Disks: RAID 60 requires a minimum of eight drives to operate efficiently. It is organized into multiple sets of parity data, similar to RAID 50, with each set consisting of at least four drives.
- Data Protection: RAID 60 offers double parity, meaning that it can withstand the failure of up to two drives within the same set of parity data. This provides a higher level of data protection compared to RAID 50.
- Write Speed: While RAID 60 still benefits from data striping, the presence of dual parity calculations can slightly impact write speeds compared to RAID 50. However, it is still suitable for many applications with moderate write workloads.
- Drive Failure Tolerance: RAID 60 is more resilient to drive failures than RAID 50, thanks to its double parity. It can handle the failure of up to two drives within a single set of parity data without data loss.
- Similar to RAID 6: RAID 60 shares similarities with RAID 6, another dual-parity RAID level, due to their double parity calculations. However, RAID 60 incorporates data striping for improved performance.
Parity Calculations: The Crucial Difference
One of the key distinctions between RAID 50 and RAID 60 lies in their parity calculations. Parity is essential for reconstructing data in the event of a drive failure.
In RAID 50, parity calculations are distributed across multiple sets of drives, with each set responsible for its own parity data. This approach provides decent data protection but is limited to a single drive failure per set.
In RAID 60, dual parity calculations are utilized within each set of drives. This means that even if two drives fail within the same set, data can still be reconstructed. This redundancy significantly enhances data protection, making RAID 60 ideal for environments where data loss is not an option.
The Role of Stripe Size
Another important factor to consider when comparing RAID 50 and RAID 60 is the stripe size. Stripe size determines the size of the data segments that are written across the drives in the array. Both RAID 50 and RAID 60 benefit from data striping, but the choice of stripe size can impact their performance and efficiency.
Smaller stripe sizes can improve read and write performance for smaller files and random access patterns. However, they can lead to increased overhead when handling larger files. Conversely, larger stripe sizes can be more efficient for larger files but might result in suboptimal performance when dealing with smaller files.
The optimal stripe size depends on the specific use case and workload of the RAID array. Organizations should carefully consider their data storage and access patterns to determine the most suitable stripe size for their needs.
Data Loss Prevention: RAID 50 vs. RAID 60
When it comes to data loss prevention, both RAID 50 and RAID 60 offer a significant level of protection. However, the key difference lies in their tolerance to drive failures.
In RAID 50, a single drive failure within a set of parity data can be recovered without data loss. This level of protection is suitable for many applications and provides peace of mind in the face of hardware failures.
In contrast, RAID 60 takes data protection to the next level by allowing for the failure of up to two drives within the same set of parity data. This double parity configuration provides an extra layer of security, making RAID 60 a preferred choice for organizations with critical data that cannot afford any downtime or data loss.

Read and Write Operations: Performance Considerations
Performance is a critical factor in choosing between RAID 50 and RAID 60. Both RAID levels offer advantages in terms of read and write operations, but there are nuances to consider.

- Read Operations: RAID 50 and RAID 60 both excel in read operations due to data striping. Data is distributed across multiple drives, allowing for parallel read access, which significantly improves read speeds. Both RAID levels are well-suited for applications that require fast data retrieval.
- Write Operations: Write performance can vary between RAID 50 and RAID 60. RAID 50 typically offers faster write speeds compared to RAID 60, making it a better choice for write-intensive workloads. However, RAID 60, with its dual parity calculations, provides higher data protection at the cost of slightly reduced write performance.
Read and Write Operations: Performance Considerations
In the battle of RAID 50 vs RAID 60, the choice ultimately comes down to your organization’s specific needs and priorities. Here’s a quick recap to help you decide:
- RAID 50 is an excellent choice for those seeking a balance between performance and data protection. It offers distributed parity calculations, suitable for environments with moderate write workloads and where a single drive failure can be tolerated.
- RAID 60 is the go-to option when data protection is paramount. It provides dual parity calculations, making it resilient against the failure of up to two drives within the same set. While it may have slightly reduced write performance compared to RAID 50, the added data security is worth it for critical applications.
Remember that both RAID 50 and RAID 60 require careful planning and consideration of factors like the number of drives, stripe size, and the type of data being stored. Whichever RAID configuration you choose, it’s essential to regularly monitor the health of your drives and implement a robust backup strategy to safeguard your data in the event of unexpected drive failures. Ultimately, the right RAID configuration will ensure your data remains accessible and secure, providing peace of mind for your organization’s data storage needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between RAID 50 and RAID 60?
RAID 50 combines RAID 5 arrays with striping for enhanced performance, while RAID 60 combines RAID 6 arrays with striping for better data protection.
How many drives do I need for RAID 50 and RAID 60?
RAID 50 typically requires a minimum of six drives, while RAID 60 needs at least eight drives to set up the arrays.
Which RAID level offers better data protection, RAID 50 or RAID 60?
RAID 60 provides superior data protection with double parity, making it more resilient to drive failures compared to RAID 50.
Is there a significant performance difference between RAID 50 and RAID 60?
RAID 50 generally offers slightly better write performance than RAID 60 due to the lower overhead of parity calculations, but the difference may not be substantial for most users.