In the realm of data storage solutions, RAID configurations play a pivotal role in determining the balance between performance, fault tolerance, and data security. RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, encompasses various levels, each designed to meet different requirements. Among these, RAID 10, often denoted as RAID 1+0, stands out as a powerhouse solution that amalgamates the strengths of other RAID levels. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of RAID levels, specifically focusing on RAID 10—its definition, advantages, disadvantages, and critical aspects of failure and data loss.
RAID 10: A Fusion of Redundancy and Performance
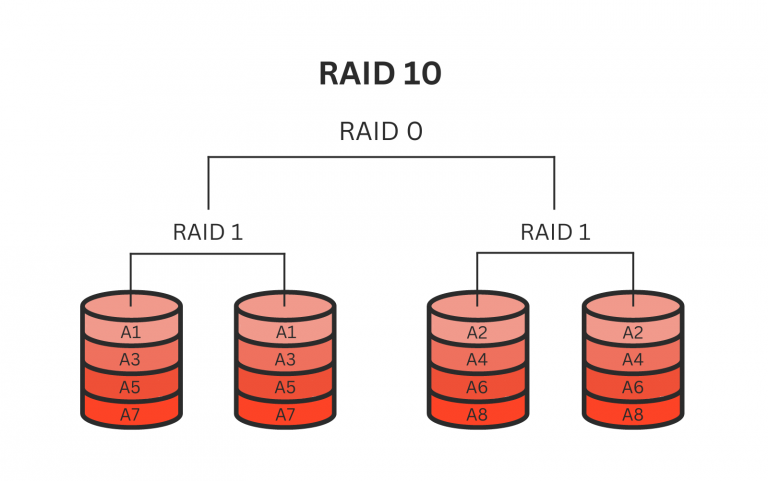
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, combines the principles of RAID 1 and RAID 0. This amalgamation results in a configuration that offers both data redundancy and improved read/write performance. In RAID 10, data is first mirrored across multiple disks, providing fault tolerance as any one drive can fail without losing data. Subsequently, these mirrored sets are striped using RAID 0, boosting the overall performance of the array. This dual-layered approach offers an ideal solution for environments that demand high-speed data access and the security of redundant storage.
Advantages of RAID 10
The advantages of RAID 10 are far-reaching and make it an enticing choice for various use cases:
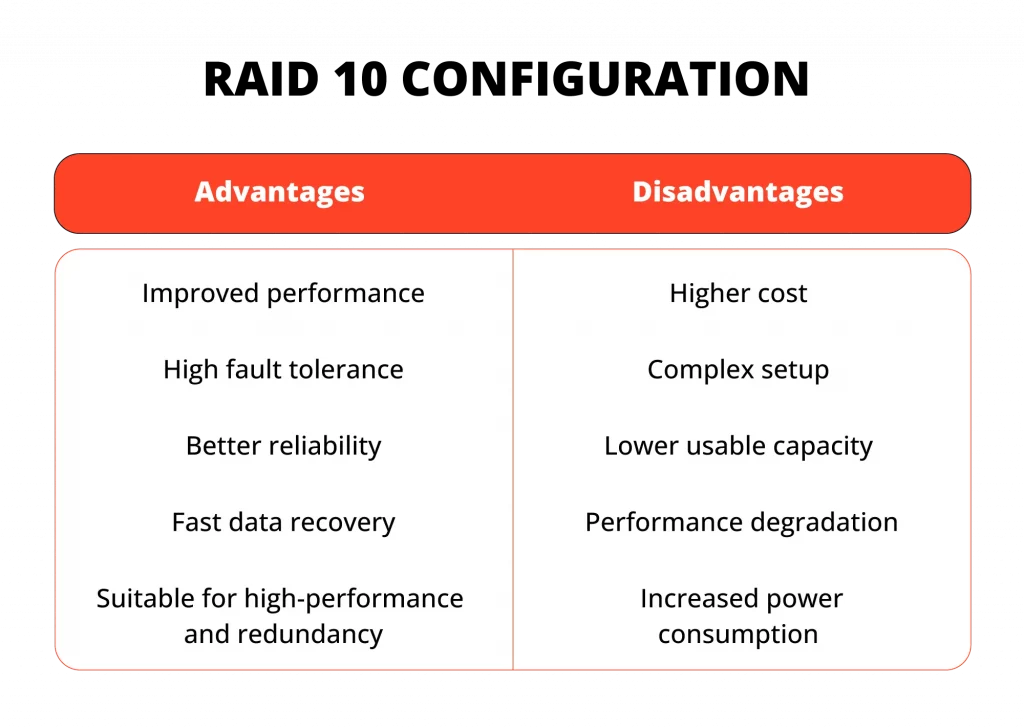
- Fault Tolerance: RAID 10 excels in fault tolerance. Since the data is mirrored, the failure of a single drive does not lead to data loss, unlike RAID 0, where a single drive failure can be catastrophic.

- Read and Write Performance: By employing RAID 0 striping, RAID 10 significantly enhances read and write operations. Data can be read from and written to multiple disks simultaneously, resulting in superior performance.
- Data Storage Efficiency: Although not as efficient as RAID 5 or RAID 6 in terms of storage utilization, RAID 10 strikes a balance by offering relatively good storage efficiency alongside its other benefits.
Disadvantages of RAID 10
While RAID 10 offers numerous advantages, it is important to consider its limitations as well:
- High Cost: Implementing RAID 10 requires a larger number of drives compared to other RAID levels. This can result in higher upfront costs for both the drives themselves and the necessary hardware.
- Reduced Capacity: Since half of the total drives are dedicated to mirroring, the usable storage capacity of the array is reduced compared to RAID levels that solely focus on striping.
- RAID 10 Failure and Data Loss: While RAID 10 provides protection against a single drive failure, simultaneous failures in both the mirrored set and the striped set can lead to data loss. Additionally, if a drive fails in one mirrored set and another drive fails in the other mirrored set before the first failure is resolved, data loss can still occur.
Mitigating RAID 10 Failure and Data Loss
To safeguard against data loss and minimize the impact of drive failures in RAID 10, it is crucial to:
Regularly Monitor Drives
Keep a vigilant eye on the health of individual drives in the array. Predictive disk monitoring tools can provide early warnings about potential drive failures.
Swift Drive Replacement
As soon as a drive failure is detected, replace the failed drive promptly. This helps in restoring redundancy and reducing the risk of further failures.
Backup Strategy
While RAID 10 provides a level of redundancy, it’s wise to maintain a comprehensive backup strategy. Backups should be stored independently from the RAID array to protect against scenarios like multiple drive failures, human errors, or disasters.
Hot Spare Drives
Integrate hot spare drives into the array configuration. These drives act as replacements for failed drives, automatically rebuilding the array without manual intervention.
In conclusion, RAID 10 stands as a robust and versatile RAID level that harmonizes the best aspects of RAID 1 and RAID 0. Its fault tolerance, impressive read and write performance, and data storage efficiency make it a compelling choice for environments that demand high-speed data access and data protection. However, the higher cost and reduced capacity should be weighed against these advantages. Implementing RAID 10 should always be accompanied by a comprehensive strategy for monitoring, maintenance, and data backup to mitigate the risks associated with drive failures and data loss.
RAID 10 Data Recovery with PITS
PITS Global Data Recovery Services stands as a reliable firm offering comprehensive RAID 10 data recovery solutions to both enterprises and individuals. Our team of engineers possesses extensive expertise in RAID systems, enabling them to effectively recover lost, corrupted, or deleted data from diverse RAID levels.
Initiating our recovery process with a risk-free assessment, we meticulously examine the affected device to discern the underlying cause of the issue.
Benefits of Our Using Services
This meticulous approach aids our engineers in pinpointing the root cause of data loss and gauging the extent of damage incurred. Leveraging the insights gleaned from this evaluation, we discern the optimal data recovery strategy tailored to the specific characteristics of the device.
With extensive years of involvement in the data recovery sector, PITS Global Data Recovery Services takes pride in boasting an impressive 99% success rate. Our primary objective revolves around ensuring our client’s satisfaction through a seamless process that guarantees safety and delivers optimal outcomes. Join the ranks of our successful clientele by initiating your RAID 10 data recovery journey with us today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RAID 10?
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, is a combination of two RAID levels: RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping). It provides both data redundancy and enhanced performance by mirroring data across drives and then striping those mirrored sets.
How does RAID 10 ensure data protection?
RAID 10 safeguards data by creating duplicate copies (mirrors) of information on multiple drives. If one drive fails, the mirrored copy ensures that data remains accessible, minimizing the risk of data loss.
What advantages does RAID 10 offer?
RAID 10 offers both speed and safety. It provides improved read/write performance due to striping while maintaining redundancy through mirroring. This combination makes it ideal for applications requiring both speed and data protection.
Are there any drawbacks to RAID 10?
While RAID 10 is robust, it can be costlier due to the need for more drives. Additionally, usable storage capacity is reduced since half of the drives are dedicated to mirroring, affecting overall cost-efficiency.
What happens if a drive fails in RAID 10?
If a drive fails in RAID 10, the mirrored copy of the data on another drive remains intact, ensuring data accessibility. However, if another drive fails before the failed drive is replaced, data loss can occur, highlighting the importance of prompt drive replacement and monitoring.
Request Help
"*" indicates required fields