RAID 5 is a popular disk redundancy technology that blends performance and data protection. As a data storage virtualization technology, RAID 5 is known for ensuring data integrity, even when one disk in the array fails. This unique capability makes RAID 5 a preferred choice for businesses and individuals who can’t afford any compromise on their data safety and accessibility.
In this blog post, we will explore what RAID 5 is, how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, and how it differs from other RAID levels.
The Basics of RAID 5 Configuration
RAID 5 is a RAID level that uses block-level striping with distributed parity. This means that data is distributed across multiple hard drives, and parity information is also distributed across those drives. Parity is used to recover data if one of the hard drives fails.
RAID 5 requires a minimum of three hard drives to function, although it can work with more. One drive is used for parity information, which is distributed across all the drives in the RAID 5 array. If a hard drive fails, the parity information can be used to rebuild the data on the failed drive.
How RAID 5 Functions
RAID 5 uses block-level striping, which means that data is distributed across all the hard drives in the array. This improves performance because data can be read and written to multiple drives simultaneously. Additionally, parity information is distributed across all the devices in the array, so there is no single point of failure.
To illustrate how RAID 5 works, imagine we have three hard drives in a RAID 5 array. When data is written to the array, it is split into blocks and distributed across the three drives. Parity information is also calculated for each block and spread across the drives. The following diagram shows an example of how data and parity information might be distributed across the drives:
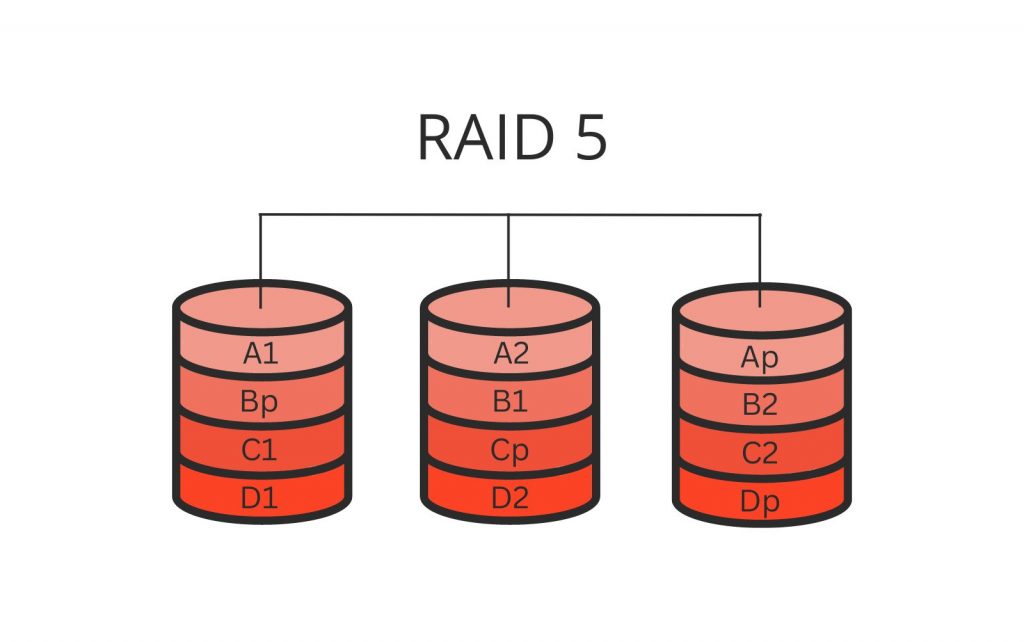
In this example, each drive contains both data blocks and parity blocks, and the parity information is distributed across all three drives. If one of the drives fails, the parity information can be used to reconstruct the missing data.
When a failed drive is replaced, the RAID 5 array will automatically rebuild the data on the new drive using the parity information. During the rebuilding process, performance may be reduced because data is being read from the other drives in the array to rebuild the missing data.
Advantages of RAID 5
- Cost-effective. RAID 5 is relatively inexpensive compared to other RAID array levels. This is due to the fact that it only requires a minimum of three hard drives.
- Good performance. RAID 5 provides good performance because data can be read and written to multiple drives at the same time.
- Fault tolerance. RAID 5 is fault-tolerant because it can withstand a single hard drive failure without losing data.
Disadvantages of RAID 5
- Rebuilding performance. When a failed drive is replaced, the RAID 5 will rebuild the data on the new drive using parity information. During the process, performance may be reduced.
- Risk of data loss. If two hard drives fail simultaneously, data may be lost because there is not enough parity information to it.
- Capacity loss. Because one drive is used for parity information, the capacity of the RAID 5 is reduced by the capacity of one drive.
| Key Features of RAID 5 | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Parity | Provides data recovery options in case of a disk failure. |
| Performance | Offers good read data transaction rates. |
| Efficient Storage | Optimizes storage by distributing parity across all disks. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Provides a cost-effective solution for improved performance and redundancy. |
| Fault Tolerance | Can withstand the loss of one disk without data loss. |
| Minimum Disk | Requires a minimum of 3 disks to set up RAID 5. |
How RAID 5 Differs from Other RAID Levels
There are several RAID levels available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. RAID 5 differs from other RAID levels in the following ways:
RAID 0
RAID 0 is not fault-tolerant because data is not duplicated or distributed across multiple drives. Instead, data is striped across multiple devices for improved performance.

RAID 1
RAID 1 duplicates data across multiple drives for increased fault tolerance. However, this comes at the cost of reduced capacity because data is duplicated on each drive.
RAID 6
RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, but it uses two sets of parity information instead of one. This provides increased fault tolerance because the array can withstand two hard drive failures without losing data.
RAID 10
RAID 10 combines the features of RAID 0 and RAID 1 by stripping data across multiple mirrored sets of drives. This provides good performance and fault tolerance but requires a minimum of four hard drives.
RAID 5 is a popular RAID level used in many businesses and organizations because of its cost-effectiveness, performance, and fault tolerance. It is a good choice for applications requiring moderate fault tolerance levels without sacrificing performance or breaking the bank. However, it is important to remember that RAID 5 is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and different RAID levels may be more appropriate for various applications.
When choosing a RAID level, it is important to consider factors such as cost, performance, capacity, and fault tolerance to find the best solution for your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the RAID 5 level?
RAID 5 is a type of data storage virtualization technology that combines disk striping with parity. It provides a robust balance between performance, data protection, and cost-effectiveness.
How does RAID 5 provide data protection?
RAID 5 uses parity information, which is spread across all the disks in the array. If a single disk fails, the system can rebuild the lost data using this parity information.
How many disks are needed for RAID 5?
A minimum of three disks is needed to set up a RAID 5 array.
What happens if more than one disk fails in RAID 5?
If more than one disk fails simultaneously in RAID 5, it can result in complete data loss. RAID 5 can only tolerate the failure of one disk.
Is RAID 5 suitable for high-volume write operations?
RAID 5 might not be the best choice for high-volume write operations because every write requires updating the parity data, which can increase the strain on the drives.
What are the main benefits of RAID 5?
RAID 5 offers good performance, efficient storage use, and excellent fault tolerance. It can also be a cost-effective solution for improved performance and redundancy.
How do you properly maintain a RAID 5 array?
Proper maintenance of a RAID 5 array includes regular monitoring of disk health and replacing any failing disks promptly.
