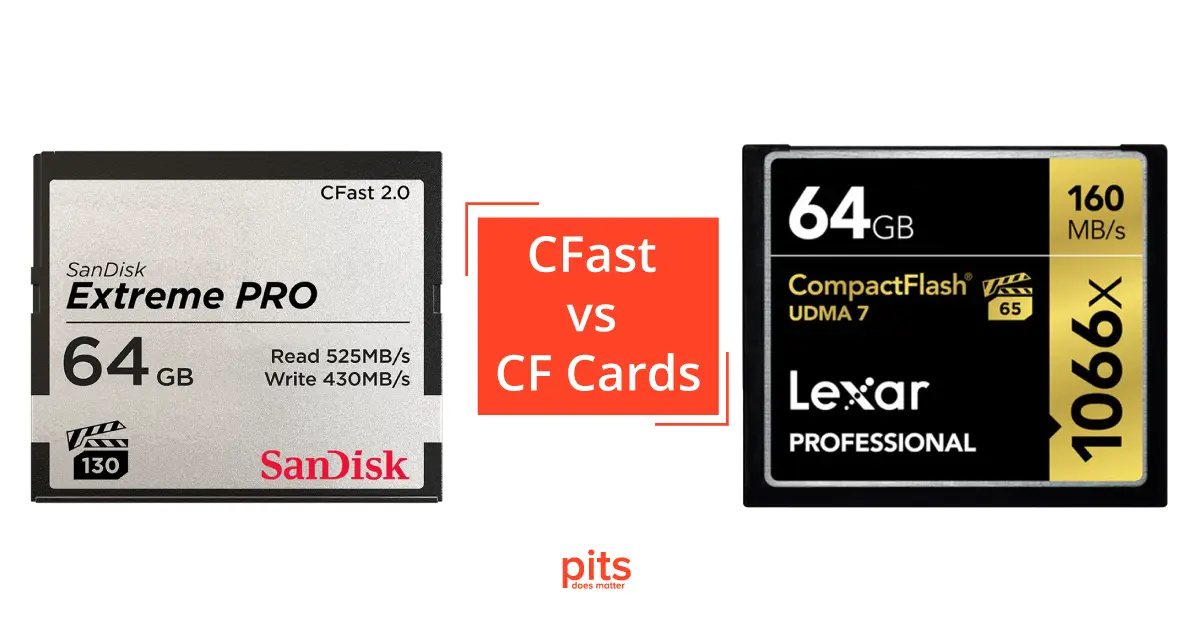
In the world of memory cards, the battle between different formats often boils down to a combination of speed, capacity, and compatibility. When it comes to CFast and CF cards, these factors play a significant role in determining which one suits your needs best. In this article, we will dive into the key differences and similarities between CFast and CF cards, shedding light on the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Understanding CF Cards and CFast Cards
CompactFlash (CF) cards and CFast cards are both popular types of memory cards commonly used in a variety of devices, such as cameras, camcorders, and other electronic devices. They share a form factor that is slightly larger than a matchbook, but that’s where the similarities start to diverge.
CompactFlash (CF) Cards: CompactFlash cards have been around since the mid-1990s and have become a staple in the digital photography world. They were initially based on the Parallel ATA (PATA) interface, which eventually gave way to faster and more efficient options.
CFast Cards: CFast, on the other hand, is a relatively newer memory card format designed to overcome the limitations of CF cards, particularly in terms of speed. CFast cards are based on the Serial ATA (SATA) interface, similar to what you might find in a traditional solid-state drive (SSD) in a computer.
Difference in Speed - CFast vs CF Cards
One of the primary differentiators between CFast and CF cards is their read and write speeds. CFast cards offer significantly faster data transfer rates compared to CF cards. While CF cards typically have a maximum transfer rate of around 167 MB/s, CFast cards, especially in their CFast 2.0 specification, can achieve much higher speeds. CFast 2.0 cards are capable of reaching speeds of up to 600 MB/s, making them ideal for high-end cameras and devices that demand swift data handling.

Form Factor and Compatibility
In terms of form factor, both CF and CFast cards share a similar physical size, which can be advantageous for devices with space constraints. However, due to differences in the underlying interface technology (PATA vs. SATA), CF and CFast cards are not cross-compatible without the use of adapters.
CFast’s SATA interface is a more modern and widely used technology, which means that CFast cards are more likely to be compatible with a broader range of devices, especially newer models. CF cards, based on the older PATA interface, might face compatibility issues with some modern devices that only support the CFast format.
Use Cases
The speed advantage of CFast cards makes them particularly suitable for high-end cameras and professional photography equipment. The faster transfer rates allow for quicker burst shooting, faster video recording, and reduced wait times for data offloading. Photographers and videographers who require top-notch performance often lean towards CFast cards to ensure seamless and efficient workflow.
On the other hand, CF cards can still find their place in devices that do not demand ultra-high-speed data transfer. Many older cameras and devices are designed to work with CF cards, and for users who don’t require lightning-fast speeds, CF cards can still offer a reliable and cost-effective storage solution.
In the showdown between CFast and CF cards, the choice ultimately comes down to your specific needs and the devices you intend to use them with.
If you are working with high-end cameras or require blazing-fast data transfer speeds, CFast cards are the clear winner. However, if you are dealing with older devices or do not require the utmost speed, CF cards can still serve you well.
It is important to consider compatibility, speed requirements, and future device upgrades when making your decision. Whichever format you choose, both CFast and CF cards have left their mark on the world of memory cards and will likely continue to play a role in data storage for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are CF cards and CFast cards?
CF cards (CompactFlash cards) and CFast cards are types of memory cards used to store data in devices like cameras and camcorders. They come in a compact size and serve as storage solutions for various electronic gadgets.
What is the main difference between CF cards and CFast cards?
The primary difference lies in their speed and data transfer capabilities. CFast cards are faster than CF cards, thanks to their modern SATA interface. CFast cards can handle data more quickly, making them suitable for tasks like rapid photo shooting and high-quality video recording.
Can I use CF cards in devices that support CFast cards, or vice versa?
Generally, CF cards and CFast cards are not directly compatible due to their different interfaces. However, you might find adapters that allow you to use one type of card in a device designed for the other type. Keep in mind that adapters could affect performance and compatibility.
What type of devices benefit from CFast cards?
CFast cards are especially beneficial for devices that demand high-speed data processing, such as professional cameras and camcorders. These cards enable faster photo bursts and smoother video recording, making them a top choice for photographers and videographers.
Are CF cards obsolete now that CFast cards are available?
CF cards are not obsolete, but their usage has become less common in favor of CFast cards. CF cards are still used in older devices or those that don’t require extremely fast data transfer speeds. CFast cards have become the preferred choice for modern high-end cameras and devices that need rapid data handling.