In the rapidly evolving world of technology, storage devices play a crucial role in determining the overall performance and speed of a computer system. Solid-state drives (SSDs) have gained immense popularity due to their superior speed, reliability, and efficiency when compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). When it comes to SSDs, two prominent storage interfaces have emerged as the primary contenders: NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) and SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment). In this blog post, we will delve into the key differences and benefits of each interface, shedding light on the ongoing battle of NVMe vs. SATA in the realm of storage interfaces.
Understanding SATA and NVMe
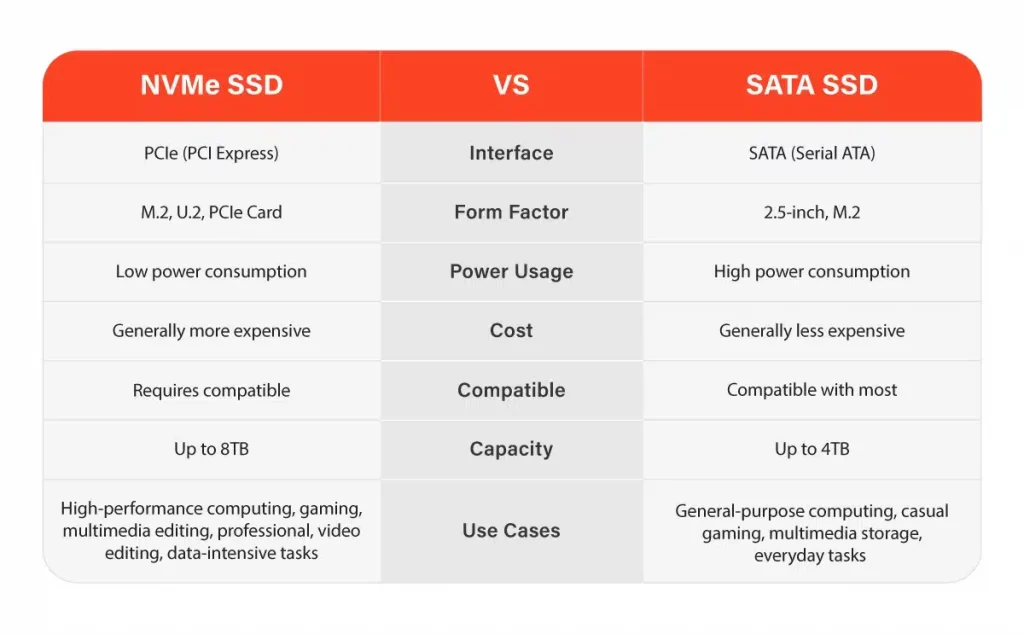
To gain a better understanding, let’s first familiarize ourselves with these two storage interfaces. SATA has been around for quite some time and has achieved widespread adoption in various storage devices. It is an advanced host controller interface that has undergone multiple revisions to improve data transfer speeds. SATA SSDs connect to the motherboard through a SATA cable and are commonly found in 2.5-inch form factor drives.
On the other hand, NVMe is a relatively new storage interface designed specifically for SSDs. It leverages the high-speed Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) interface, commonly used for connecting graphics cards and other high-performance peripherals. NVMe SSDs are predominantly found in the compact M.2 form factor, allowing them to be directly attached to the motherboard.
Speed and Performance
One of the primary differentiating factors between NVMe and SATA is their data transfer speeds. SATA SSDs are limited by the maximum bandwidth provided by the SATA interface, which is around 6 gigabits per second (Gbps) for the latest SATA revision. Consequently, the theoretical maximum sequential read and write speeds for SATA SSDs reach approximately 550 megabytes per second (MBps).

In contrast, NVMe SSDs harness the power of the PCIe interface, offering significantly higher data transfer speeds. The latest NVMe drives can achieve speeds of up to 7000 MBps for sequential reads and 5000 MBps for sequential writes.
This substantial speed advantage makes NVMe drives the preferred choice for tasks that demand high-performance storage, such as video editing, gaming, and professional applications.
Form Factors and Flexibility
Form factor and flexibility are essential aspects to consider when comparing these storage interfaces. SATA SSDs traditionally come in the 2.5-inch form factor, making them suitable for both desktop and laptop installations. However, the introduction of the M.2 SATA form factor has brought about more flexibility by allowing direct attachment to the motherboard without the need for cables.
NVMe drives, on the other hand, are primarily available in the M.2 form factor. This compact design saves space and simplifies the installation process, particularly in smaller systems such as ultrabooks and mini-PCs. Additionally, some high-end motherboards feature multiple M.2 slots, enabling users to leverage the power of RAID configurations with NVMe drives for even faster performance.
Compatibility and Future-Proofing
When it comes to compatibility, SATA drives have the upper hand due to their widespread adoption. SATA interfaces are supported by nearly all modern motherboards, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of systems. This makes it easier for users to upgrade their storage without worrying about compatibility issues.
While NVMe drives require a motherboard with support for the PCIe interface and an M.2 slot, the adoption of NVMe is rapidly increasing. Many modern motherboards come with built-in M.2 slots that support NVMe drives, making it easier for users to take advantage of faster speeds and improved performance. As technology advances, we can expect to see NVMe becoming the standard for storage interfaces, gradually phasing out SATA.
Price and Value
The price-to-performance ratio is an important consideration when making any technology purchase. SATA SSDs have been on the market for a longer period and have become more affordable compared to NVMe drives. This affordability makes SATA SSDs a viable choice for users who prioritize storage capacity over sheer speed.
NVMe drives, on the other hand, are generally more expensive than SATA drives. However, the price difference is gradually narrowing as NVMe technology becomes more prevalent. If you require high-performance storage for demanding tasks, the extra investment in an NVMe drive is undoubtedly worth it. In the battle of storage interfaces, NVMe and SATA offer distinct advantages based on specific needs. SATA SSDs continue to serve as reliable storage solutions, providing good performance, affordability, and compatibility with a wide range of systems.
However, NVMe drives provide a significant leap in speed and performance, making them ideal for power users and professionals who require high-performing storage devices.
As technology progresses and NVMe becomes more widely adopted, we can expect to see a gradual shift towards NVMe drives in the coming years. Whether you choose NVMe or SATA, both options provide solid-state storage solutions that outperform traditional hard drives and enhance the overall computing experience. Consider your requirements, budget, and system compatibility to make an informed decision when selecting your storage interface.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between NVMe and SATA?
The primary difference lies in their data transfer speeds and the interfaces they utilize. NVMe leverages the high-speed PCIe interface, offering significantly faster speeds compared to SATA, which relies on the SATA interface.
Can I use an NVMe SSD in place of a SATA SSD?
Yes, you can use an NVMe SSD in place of a SATA SSD as long as your motherboard supports NVMe drives. However, it’s important to note that NVMe drives require an M.2 slot, so you may need to check if your system has an available M.2 slot or use an adapter if your motherboard supports it.
Can I use NVMe and SATA drives together in the same system?
Yes, it is possible to use both NVMe and SATA drives in the same system, as long as your motherboard has the necessary slots and ports. You can install the NVMe drive in the M.2 slot and connect SATA drives to the available SATA ports on your motherboard. This allows you to benefit from the speed of NVMe for certain applications while utilizing the cost-effective storage capacity of SATA drives for others.
Can I upgrade from a SATA SSD to an NVMe SSD without changing my operating system?
Yes, it is possible to upgrade from a SATA SSD to an NVMe SSD without reinstalling the operating system. However, you would need to check if your motherboard supports NVMe drives and has an available M.2 slot. You can then clone your existing SATA SSD to the NVMe SSD using specialized software to transfer your operating system and data seamlessly.
How do NVMe drives achieve faster speeds than SATA drives?
NVMe drives utilize the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface, which offers higher bandwidth and faster data transfer rates compared to the SATA interface. This allows NVMe drives to leverage the full potential of solid-state storage technology, enabling them to deliver exceptional performance.
Request Help
"*" indicates required fields