In the world of data storage, RAID (Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks) configurations play a crucial role in enhancing performance and providing data redundancy or fault tolerance. RAID 0, in particular, is known for its ability to unleash speed and performance like no other. In this article, we will delve into the workings of RAID 0, its advantages and disadvantages, and how it compares to other RAID levels.
Understanding RAID 0
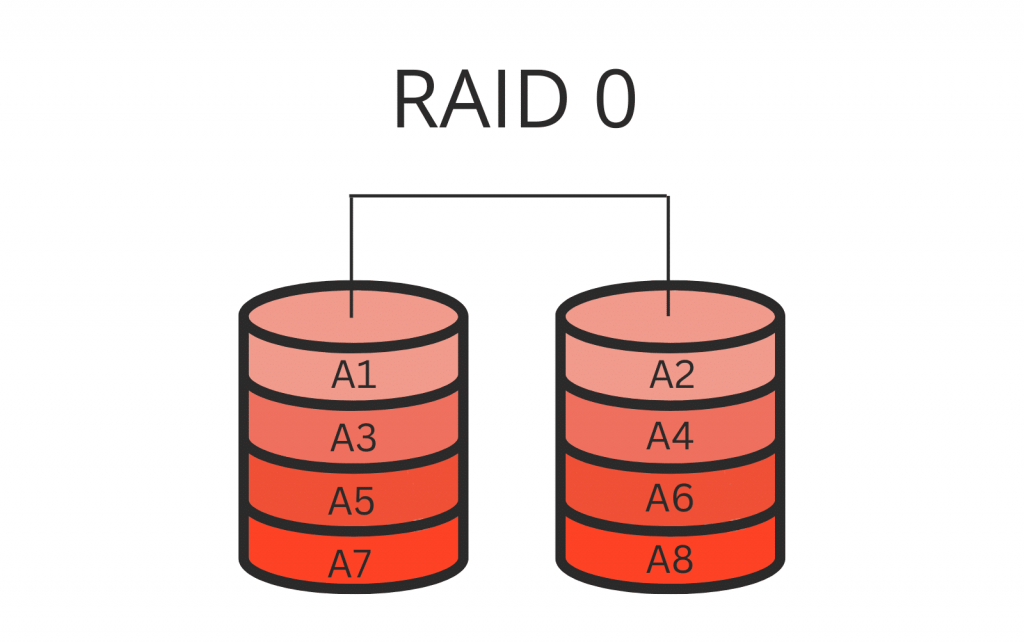
RAID 0 is a specific RAID level that focuses on maximizing speed and performance. Unlike other RAID levels that emphasize data redundancy, RAID 0 distributes data across multiple disks without any redundancy or fault tolerance mechanisms. It is sometimes referred to as a “striping” technique.
In RAID 0, multiple drives are combined into a single logical unit called a RAID 0 array. Instead of writing data to a single drive, RAID 0 divides the data into smaller chunks, known as stripes, and distributes them across the drives in the array. This parallelization of data allows for simultaneous read and write operations across the drives, resulting in significantly higher read and write speeds compared to a single drive.
Advantages of RAID 0
RAID 0 offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for users seeking enhanced speed and performance in their data storage solutions. Here are five key advantages of RAID 0:
- High Speed and Performance: RAID 0 excels in delivering superior read and write speeds compared to a single drive configuration. By striping data across multiple drives and allowing simultaneous access to those drives, RAID 0 significantly improves data transfer rates. This makes it an excellent choice for tasks that require quick and efficient data processing, such as video editing, large file transfers, and database operations.
- Increased Storage Capacity: RAID 0 combines the storage capacity of multiple drives into a single logical unit. As a result, the total storage capacity of the RAID 0 array is the sum of the capacities of all the individual drives. This is particularly beneficial for users dealing with large datasets that require ample space. The increased storage capacity allows for seamless expansion and accommodates growing data storage needs.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Compared to other RAID levels that focus on data redundancy and fault tolerance, RAID 0 is a cost-effective solution. It does not require additional drives for mirroring or parity information, reducing the overall hardware costs associated with setting up a RAID array. If data redundancy is not a critical requirement for your specific use case, RAID 0 provides an economical choice with significant performance gains.
- Simplified RAID Configuration: Implementing RAID 0 is relatively straightforward. It does not involve complex configurations or the need for a dedicated RAID controller. Most modern operating systems have built-in support for RAID 0, allowing users to easily set it up using software-based RAID configurations. This simplicity makes RAID 0 more accessible to a wider range of users, including enthusiasts and small-scale businesses.
- Low Latency and Quick Response Times: Due to its data striping approach, RAID 0 reduces latency and provides quick response times. The parallelization of data across multiple drives allows for efficient data retrieval and faster access. This benefit is particularly advantageous in scenarios that require frequent and simultaneous data access, such as real-time data processing, high-demand applications, and database-driven systems.
Disadvantages of RAID 0
While RAID 0 offers impressive speed and performance benefits, it also comes with several disadvantages that users should be aware of before implementing it. Here are five key disadvantages of RAID 0:
- No Data Redundancy: Unlike other RAID levels that provide data redundancy and fault tolerance, RAID 0 does not offer any form of data redundancy. If a single drive in the RAID 0 array fails, there is no built-in mechanism to recover the lost data. This lack of redundancy makes RAID 0 vulnerable to data loss and increases the risk of complete data loss if a drive fails.
- Increased Risk of Data Loss: Due to the absence of data redundancy, RAID 0 carries a higher risk of data loss compared to other RAID levels. If any drive in the array fails, all the data stored across the entire array is at risk. This risk is particularly significant when dealing with large amounts of critical or irreplaceable data, such as important documents, customer information, or valuable media files.
- Decreased Reliability: RAID 0 arrays are more susceptible to drive failures compared to other RAID configurations. Since RAID 0 does not provide redundancy, the failure of a single drive can have a catastrophic impact on the entire array. This reduced reliability makes RAID 0 less suitable for applications or environments where data integrity and continuous operation are crucial.

- Limited Fault Tolerance: RAID 0 lacks fault tolerance capabilities. In the event of a drive failure, there is no built-in mechanism to recover or rebuild the data. This means that the failure of a single drive can result in immediate data loss, without any chance of retrieving the lost information. This limitation makes RAID 0 less suitable for applications that require high levels of data availability and protection.
- Inability to Combine Drive Sizes: In RAID 0, all drives within the array must have the same capacity. This limitation restricts the ability to combine drives of different sizes, as the array’s overall capacity will be limited to the size of the smallest drive. This can be problematic when trying to optimize storage capacity or when upgrading drives in the future.
RAID 0 vs. Other RAID Levels
When comparing RAID 0 to other RAID levels, such as RAID 1 (mirroring) or RAID 5 (striping with parity), the key difference lies in the approach to data redundancy. While RAID 1 and RAID 5 provide fault tolerance by either mirroring data or using parity information, RAID 0 focuses solely on performance and speed.
RAID 0 can outperform other RAID levels in terms of read and write speeds due to its parallelization of data across multiple drives. However, it lacks the data redundancy that makes RAID 1 and RAID 5 more reliable in the event of a drive failure.
RAID 0 is a RAID level that emphasizes speed and performance by striping data across multiple drives. It provides high-speed read and write operations, making it ideal for tasks that require intensive data processing. However, it lacks data redundancy, making it more susceptible to data loss if a drive fails. It’s important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of RAID 0 carefully and consider the specific needs of your data storage environment before implementing it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RAID 0 and how does it work?
RAID 0 is a RAID level that focuses on performance by striping data across multiple drives. It divides data into smaller chunks called stripes and distributes them across the drives in the array. This parallelization allows for simultaneous read and write operations, resulting in increased speed and performance.
Does RAID 0 provide data redundancy or fault tolerance?
No, RAID 0 does not provide data redundancy or fault tolerance. It sacrifices redundancy to maximize speed and storage capacity. If a single drive fails in a RAID 0 array, all the data stored across the entire array is at risk of being lost.
What are the advantages of RAID 0?
RAID 0 offers high-speed data transfer rates, making it ideal for tasks that require intensive data processing. It also provides increased storage capacity by combining the capacities of multiple drives. RAID 0 is cost-effective and relatively easy to set up, as it does not require a dedicated RAID controller.
What are the disadvantages of RAID 0?
The primary disadvantage of RAID 0 is the lack of data redundancy. In the event of a drive failure, data loss is highly likely. RAID 0 arrays are also more vulnerable to drive failures compared to other RAID levels that offer redundancy. Additionally, RAID 0 cannot combine drives of different sizes, and the failure of a single drive can result in the loss of all data associated with it.
Is RAID 0 suitable for all types of data storage needs?
No, RAID 0 is not suitable for all scenarios. It is best suited for applications where speed and performance are the top priorities, and data redundancy is not critical. It is commonly used in gaming, video editing, and other data-intensive tasks. However, for applications that require data protection and fault tolerance, other RAID levels like RAID 1 or RAID 5 would be more appropriate.
Request Help
"*" indicates required fields
