Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks, commonly known as RAID, are a critical component of data storage solutions in modern IT environments. RAID levels play a crucial role in protecting data from disk failures and ensuring high availability. Two popular RAID levels, RAID 6 and RAID 10, offer distinct advantages and are often compared when deciding on a storage configuration. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the differences between RAID 6 and RAID 10, considering factors like disk capacity, data loss prevention, disk utilization, and more.
Understanding RAID 6 and RAID 10 Levels
Before we dive into the specifics of RAID 6 and RAID 10, let is briefly review what RAID levels are:
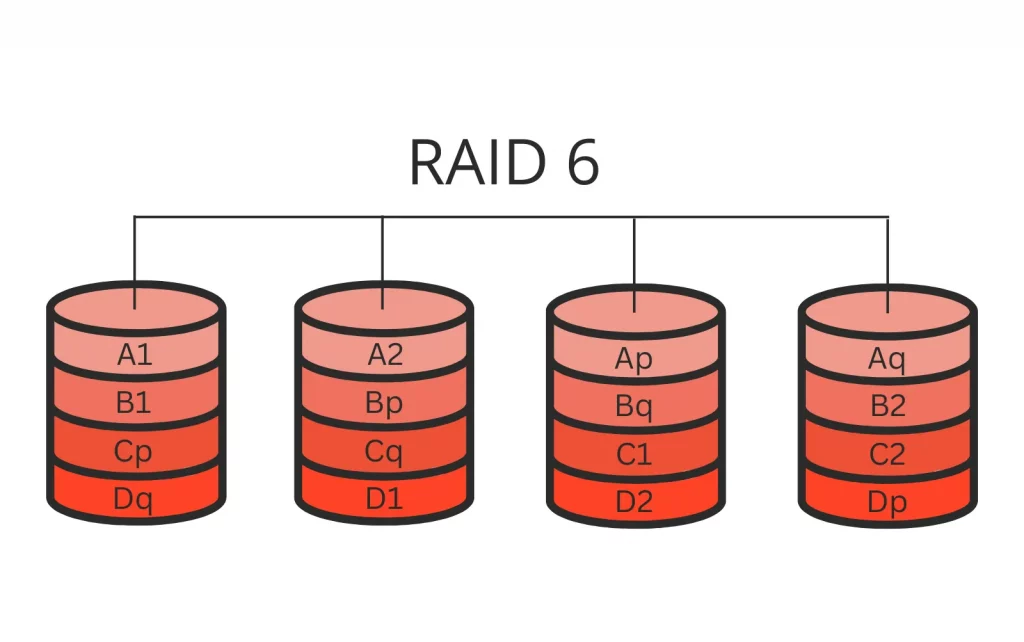
- RAID 6: RAID 6 is a nested RAID level that uses double parity to protect data. It is designed to withstand the failure of up to two disks without data loss. This is achieved by calculating parity across all the disks in the array.
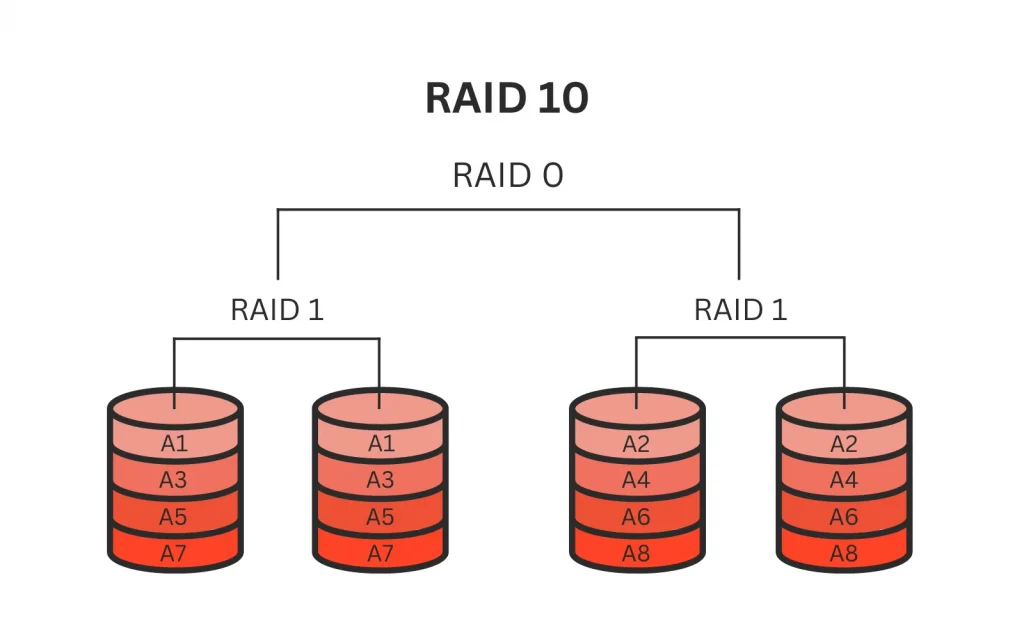
- RAID 10: RAID 10, often referred to as RAID 1+0, combines the features of RAID 1 and RAID 0. It mirrors data across multiple disk pairs and then strips these pairs for performance. RAID 10 offers excellent redundancy and performance.
Disk Capacity and Disk Utilization
One of the primary considerations when choosing a RAID level is disk capacity and utilization. RAID 6 typically offers better disk capacity utilization compared to RAID 10. In RAID 6, you can use most of the available disk space for data storage, as parity information is spread across all disks. However, in RAID 10, you sacrifice some capacity for mirroring data across disk pairs.

Data Loss Prevention
When it comes to preventing data loss due to disk failures, both RAID 6 and RAID 10 excel but they use different methods:
- RAID 6: With its double parity scheme, RAID 6 can survive the simultaneous failure of two disks in the array without losing data. This makes it a robust choice for data integrity.
- RAID 10: RAID 10 offers high redundancy as well, but it can only tolerate one drive failure in each mirrored pair. However, it provides superior performance during rebuilds compared to RAID 6.
Hot Spare and Rebuild Times
RAID 6 and RAID 10 also differ in terms of hot spares and rebuild times:
- RAID 6: Because it can withstand two disk failures, RAID 6 might not require hot spares as frequently as RAID 10. Rebuilding the array after a disk failure can be time-consuming due to the need to recalculate double parity.
- RAID 10: RAID 10 arrays usually require hot spares for quick recovery after a drive fails. Rebuild times are generally faster compared to RAID 6 because only one disk per mirrored pair needs to be rebuilt.
Consider Your Use Case
When choosing between RAID 6 and RAID 10, it is essential to consider your specific use case and requirements:
- If you prioritize capacity and can tolerate longer rebuild times, RAID 6 might be suitable for your needs, especially in environments with large storage spaces.
- If performance and faster rebuilds are critical, RAID 10 is an excellent choice, but you’ll need more disks to achieve the same capacity as RAID 6.
In the battle of RAID 6 vs. RAID 10, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. The choice ultimately depends on your specific storage needs, including factors like disk capacity, data loss tolerance, and performance requirements. Both RAID 6 and RAID 10 offer robust solutions for redundant arrays of independent disks, and understanding their differences is key to making an informed decision for your data storage strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RAID 6, and how does it compare to RAID 10 in terms of data protection?
RAID 6 is a redundant array of independent disks that uses double parity to protect data. It can withstand the simultaneous failure of up to two disks without data loss. RAID 10, on the other hand, offers data protection through mirroring and striping, but it can only tolerate one drive failure in each mirrored pair.
Which RAID level is better for maximizing disk capacity: RAID 6 or RAID 10?
RAID 6 is more efficient in terms of disk capacity utilization as it uses double parity. This means that you can typically store more data on RAID 6 compared to RAID 10 for the same number of disks.
What are the considerations for performance when choosing between RAID 6 and RAID 10?
RAID 10 generally offers better performance compared to RAID 6. This is because RAID 10 strips data across mirrored pairs, providing faster read and write speeds. RAID 6, while reliable, may have slower performance due to its parity calculations.
How do RAID 6 and RAID 10 handle rebuild times after a disk failure?
RAID 6 rebuilds can be time-consuming because they involve recalculating double parity. RAID 10, on the other hand, typically has faster rebuild times because only one disk per mirrored pair needs to be rebuilt.
