In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, one aspect that continues to push the boundaries is storage. The need for faster, more efficient, and higher-capacity storage solutions has given rise to the M.2 SSD, a compact yet powerful storage device that has quickly gained popularity among tech enthusiasts, gamers, and professionals alike. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of M.2 SSDs, their benefits, how they work, and potential data loss risks associated with these cutting-edge storage solutions.
What is an M.2 SSD?
To understand the significance of M.2 SSDs, let’s start with the basics. M.2 stands for “Next Generation Form Factor” (NGFF), and it is a small form factor that was designed to accommodate a variety of devices, including SSDs. Unlike traditional SATA drives that are connected through cables, M.2 SSDs are plugged directly into the motherboard, utilizing the M.2 connector.
M.2 SSDs come in various lengths and widths, known as “keys,” which determine the interface and functionality of the device. They can be as short as 16mm and as long as 110mm. The two most common keys for M.2 SSDs are B and M, with the B key supporting SATA and PCIe x2 interfaces and the M key supporting PCIe x4 interfaces.

M.2 SSDs utilize two primary interfaces: SATA and PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express). SATA M.2 SSDs are similar in functionality to their traditional 2.5-inch SATA counterparts. They use the same SATA interface and offer speeds comparable to regular SATA drives, making them a suitable option for users who seek an upgrade without needing to replace their motherboard.
On the other hand, NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs, which use the PCIe interface, are the real game-changers. NVMe is a protocol designed specifically for flash memory, which is the core component of SSDs. This protocol leverages the full potential of high-speed PCIe lanes, providing significantly faster transfer speeds compared to SATA. As a result, NVMe M.2 SSDs can deliver exceptional performance, making them ideal for tasks that demand rapid data access, such as gaming, content creation, and video editing.
Benefits of M.2 SSDs
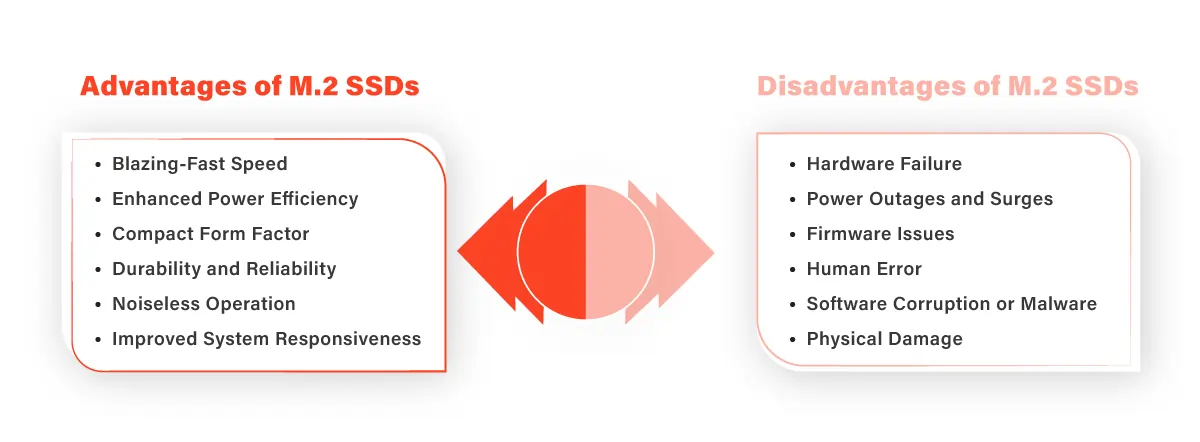
The transition from traditional disk drives to Solid State Drives (SSDs) was a massive leap in terms of speed and reliability, and M.2 SSDs take that leap even further. Here are some key benefits of M.2 SSDs:
- Speed and Performance:
M.2 SSDs, especially those using the NVMe protocol, offer remarkable speed improvements over traditional SATA drives. With transfer speeds that can exceed 3000 MB/s, tasks like booting up your operating system, launching applications, and transferring large files become incredibly swift.

- Compact Form Factor:
The small form factor of M.2 SSDs allows them to fit seamlessly into modern devices, including ultrabooks, compact desktops, and even some high-end laptops. This compactness not only saves space but also opens up possibilities for sleeker and more portable designs.
- Efficiency and Reliability:
M.2 SSDs are built using flash memory, which is more reliable and durable compared to traditional spinning hard drives. They have no moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure and allowing for quieter operation. Additionally, M.2 SSDs generate less heat, contributing to the overall efficiency and lifespan of the device.
- Compatibility:
M.2 slots are becoming increasingly common on modern motherboards. This means that users have the flexibility to choose between SATA and NVMe M.2 SSDs based on their requirements. Even if your motherboard supports only SATA M.2, the performance improvement over traditional SATA drives is still significant.
Data Loss Risks on M.2 SSDs
While M.2 SSDs offer numerous advantages, it is essential to be aware of potential risks, including data loss. The characteristics that make M.2 SSDs efficient and fast can also contribute to certain vulnerabilities:
1
Limited Lifespan of Flash Memory
All SSDs, including M.2 variants, have a finite number of write cycles that each memory cell can endure. This limitation is due to the nature of flash memory, which can wear out over time. While modern SSDs employ wear-leveling algorithms to distribute write cycles evenly across the cells, it’s crucial to keep track of the SSD’s health using tools provided by the manufacturer.
2
Sudden Data Loss
Unlike traditional mechanical hard drives that often display signs of impending failure, SSDs can experience sudden and catastrophic failures. While this is relatively rare, it highlights the importance of maintaining regular backups of your data. In the event of an SSD failure, having a backup ensures that your critical files are not lost forever.
3
Firmware and Compatibility Issues
M.2 SSDs require proper firmware updates to ensure stability, security, and performance improvements. Failing to update the firmware or encountering compatibility issues during the update process can potentially lead to data corruption or loss. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines when updating your SSD’s firmware.
4
Power Loss Vulnerabilities
Power loss during data writes can lead to data corruption, especially if the SSD’s power-loss protection mechanisms are inadequate. Some NVMe SSDs have built-in capacitors that provide enough power to finish ongoing write operations in case of a sudden power loss. However, not all M.2 SSDs have this feature, so it is wise to consider this aspect when making a purchase decision.
The M.2 SSD represents a significant step forward in the realm of storage devices, providing faster speeds, smaller form factors, and enhanced efficiency compared to traditional SATA drives. With the flexibility to choose between SATA and NVMe interfaces, users can tailor their storage solutions to meet their specific needs. However, like any technology, M.2 SSDs come with their own set of considerations, including data loss risks that stem from the characteristics that make them so efficient and powerful. By understanding these risks and implementing proper backup and maintenance strategies, users can fully harness the potential of M.2 SSDs while safeguarding their valuable data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an M.2 SSD?
An M.2 SSD is a small, flat storage device that fits directly onto a computer’s motherboard. It is like a super-fast hard drive that helps your computer run faster and store data.
How does an M.2 SSD work?
M.2 SSDs work by using flash memory, a fast type of storage that doesn’t have moving parts like old hard drives. They plug into special slots on the motherboard, and they can transfer data really quickly, making your computer faster.
What is the difference between SATA and NVMe M.2 SSDs?
SATA M.2 SSDs are like regular hard drives but smaller and faster. NVMe M.2 SSDs are even faster because they use a special protocol that takes full advantage of your computer’s speed.
Are M.2 SSDs better than regular hard drives?
Yes, M.2 SSDs are much better than regular hard drives. They’re faster, quieter, and more reliable because they don’t have spinning parts. They can make your computer start up quickly, load games faster, and save files more speedily.
Can I use an M.2 SSD with my computer?
It depends. If your computer has an M.2 slot on the motherboard, you can use an M.2 SSD. Just make sure to check if you need SATA or NVMe, and also look at the size (length) of the SSD to see if it fits. If you are not sure, you can ask a computer expert or check your computer’s manual.
Request Help
"*" indicates required fields
