In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the reasons why servers crash, a common problem that disrupts operations and causes significant downtime. Understanding the root causes of server downtime is key for IT professionals, system administrators, and business owners to create effective prevention and recovery plans. We’ll explore everything from hardware malfunctions and software conflicts to external threats like cyber-attacks and power failures, identifying the main factors behind server crashes.
What is a Server Crash
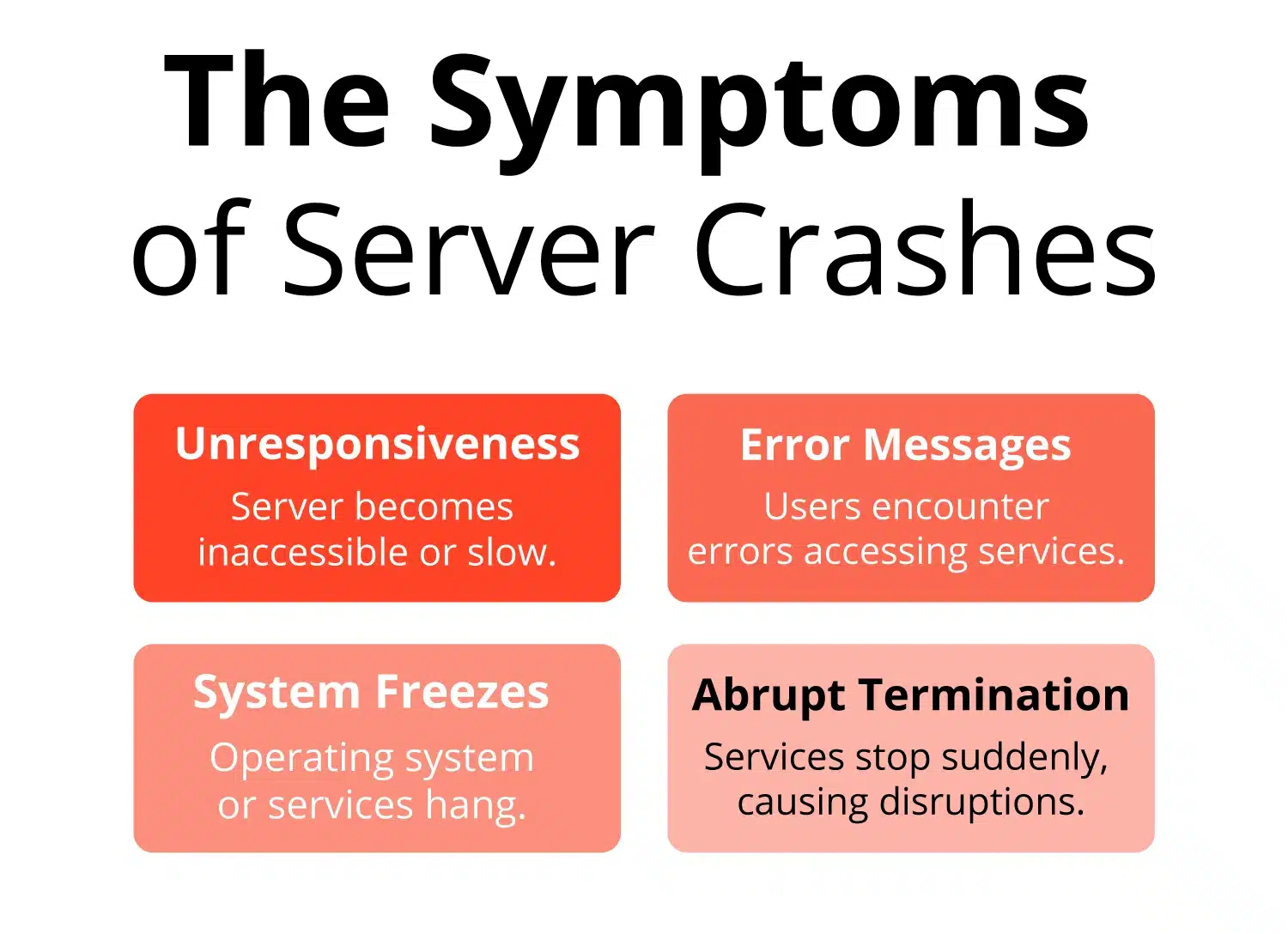
A server crash happens when a computer stops responding due to an unexpected hardware failure or software issue. This can result in the complete shutdown of the server, leading to data loss and service disruptions.
Server crashes are often caused by software or hardware malfunctions, but external factors can also play a significant role. Servers are the backbone of the internet and business operations, handling websites, email, databases, and cloud storage.
Hardware Failures as a Cause for Server Crashes
One primary reason a server is down is hardware failure. Hardware failures represent a significant threat to server stability, often resulting in unexpected crashes that can disrupt business operations and cause to data loss. Unlike software issues that might be resolved with a patch or an update, hardware malfunctions usually require physical intervention, whether it’s repair or replacement, making them particularly disruptive.
Hard Drive Failures
Hard drives are critical for data storage, and their failure can cause entire systems to crash. Common signs include frequent freezing, corruption of files, and unusual noises. Regular monitoring of SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) status can help predict failures.

CPU Overheating
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the server, and overheating can lead to automatic shutdowns to prevent damage. Maintaining optimal cooling through proper ventilation, using high-quality cooling systems, and regular cleaning of air filters can mitigate this risk.
Motherboard Issues
The motherboard connects all of a server’s components, and issues here can lead to complete system failures. Causes range from physical damage to electrical faults. Preventive measures include ensuring a clean, stable power supply and avoiding physical shock or damage during maintenance.
The Role of Software in Server Stability
Software issues represent another critical vector that can lead to server crashes, affecting stability and performance. Unlike hardware, which might require physical repair or replacement, software problems often stem from conflict, corruption, or misconfiguration. Key aspects that contribute to software-induced crashes include:

- Incompatibility occurs when different software applications or software and hardware don’t work well together. Regular updates and ensuring compatibility between software versions and hardware components are essential.
- Corrupt Files or Applications: Corruption can occur for various reasons, from incomplete updates to malware. Corrupt files may prevent the server from booting up correctly or lead to crashes during operation.
- Resource Leakages: Poorly optimized or designed software may consume disproportionate amounts of system resources, such as memory (RAM) or processing power (CPU), leading to server overload and potential crashes. Monitoring tools can help identify and rectify these leakages.
Accidental configuration changes or software updates can sometimes unintentionally crash servers, causing widespread disruption to network services.
Overloading and Server Performance
Server overloading is a primary factor contributing to performance degradation and crashes. It occurs when the server’s demand exceeds its processing capacity, leading to slow response times or total failure. Overloading can stem from a surge in web traffic, excessive data processing tasks, or running too many applications simultaneously. The consequences can be severe, impacting user experience and potentially leading to data loss and significant downtime.
Another major cause of servers stopped responding is external threats such as cyber-attacks and power failures. Hackers often target servers to gain access to sensitive data or disrupt operations, resulting in a complete system crash. Power outages can also lead to server downtime, especially if there is no backup power source or proper shutdown procedures in place.
Best Practices for Preventing Server Crashes
Preventing server crashes necessitates a proactive approach, focusing on regular maintenance, diligent monitoring, and strategic planning. By adopting a comprehensive set of best practices, organizations can significantly minimize the risk of server downtime and ensure their digital infrastructure remains robust and reliable.
Routine Maintenance
Establish a schedule for regular hardware inspections and software evaluations to catch potential issues early. This includes cleaning dust from hardware components, checking for hardware wear and tear, and reviewing software logs for errors.
Comprehensive Security Solutions
Implement strong security measures such as malware scanners and intrusion detection systems to prevent crashes or data breaches.
Access Control
Limit server access to authorized personnel only, reducing the risk posed by human error or malicious activity.
Employ strong authentication methods and regularly audit access logs for suspicious activity.
Regular Backups

Implement a regular, automated backup regime to secure critical data. Ensure backups are stored in multiple, geographically dispersed locations to protect against data loss from hardware failures or natural disasters.
Installing a RAID configuration on your server is crucial for minimizing downtime and protecting against data loss. If you notice any indicators of RAID failure, contact a professional RAID data recovery service immediately.
For those seeking a dependable solution to safeguard against server crashes and ensure the integrity of your data, PITS Global Data Recovery Services stands ready to assist. Our team of experts specializes in Server data recovery, offering swift, efficient, and confidential services to mitigate downtime and secure your critical information. For more information on how we can help protect your digital infrastructure and recover from any potential server crashes, contact us today.
FAQ about Server Crashes
What causes a server to crash?
Server crashes can result from various factors, including software incompatibility, corrupt files, resource leakages, overloading, cyber-attacks, and power failures. Ensuring software compatibility, maintaining server hygiene, and implementing robust security measures are critical to prevent crashes.
How can the overloading of a server be prevented?
Preventing server overloading involves employing load-balancing techniques to distribute traffic evenly across servers and conducting server capacity planning to anticipate and meet future demands. Additionally, optimizing applications to run more efficiently can reduce the load on servers.
What are the best practices for ensuring server security?
Enhancing server security involves:
- Implementing robust measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
- Restricting access to authorized personnel.
- Using stringent authentication methods.
- Consistently monitor access logs for unusual activities.
How often should servers be backed up?
Servers should be backed up regularly, with the frequency depending on the volume of data and how often it changes. Implementing an automated backup regime that stores backups in multiple, geographically dispersed locations can protect against data loss.
What should I do if I suspect a RAID failure?
If you suspect a RAID failure, it is crucial to avoid attempting a self-repair as it can lead to further data loss. Contacting a professional RAID data recovery service, such as PITS Global Data Recovery Services, immediately is recommended to ensure the highest chance of recovering your data safely and efficiently.