What are Nested RAID Levels? The levels of RAID are crucial for improving data redundancy and overall performance. As the need for data storage solutions continues to rise, it becomes evident that we need more sophisticated systems to safeguard our data. This is where nested RAID levels play a crucial role. We can achieve exceptional performance and fault tolerance by combining the benefits of multiple standard RAID configurations. In this blog post, we’ll explore the complexities of nested RAID levels. We’ll provide insights into their functionality, benefits, and recommended configurations to fulfill your data storage requirements.
Understanding Nested RAID
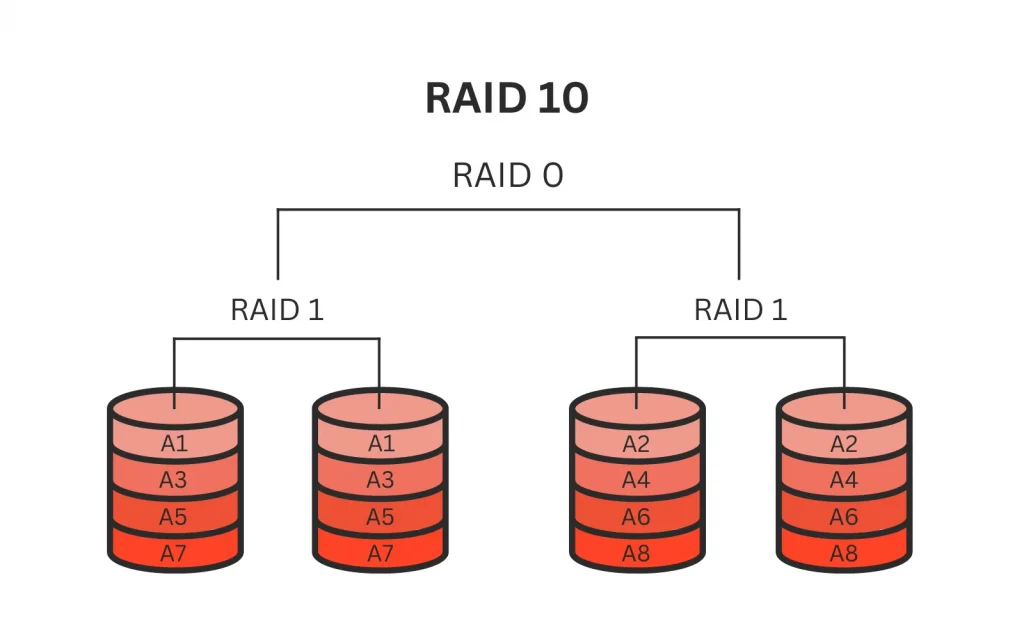
Nested RAID, also known as hybrid RAID, is a technique that combines multiple standard RAID levels to enhance both data redundancy and performance. To illustrate this concept, let’s consider RAID 10 as an example. RAID 10 is a nested RAID level that combines the features of RAID 1 and RAID 0. In this configuration, RAID 1 provides redundancy through mirroring, while RAID 0 improves performance with striping. It ensures that even if one disk fails, the data remains intact due to the presence of its mirrored copy.
In addition to RAID 10, other popular nested RAID configurations exist, such as RAID 01, RAID 50, and RAID 60. Each of these configurations has its unique strengths and use cases.
Nested RAID is a remarkable storage solution that balances data protection and performance. Although it may require more disks than standard RAID levels, the advantages of enhanced fault tolerance and performance make it extremely valuable.

Organizations can construct a highly efficient and reliable storage system by carefully choosing the suitable nested RAID level according to specific requirements for data protection, speed, and capacity. It ensures that we prioritize data integrity and performance, resulting in an optimal storage solution for any organization.
Advantages of Nested RAID Levels
Nested RAID levels provide various benefits, making them an appealing data storage and management option. Combining the advantages of different RAID configurations offers redundancy, enhanced performance, and strong fault tolerance. Some of the main benefits include:
Improved Fault Tolerance: Nested RAID configurations offer superior fault tolerance by combining multiple layers of redundancy. This ensures data accessibility and safeguards against loss, even during numerous disk failures.

Increased Performance: Nested RAID configurations boost performance by combining the advantages of different RAID levels, enhancing data access speeds, read/write operations, and overall system efficiency.
Customization Options: Nested RAID levels offer flexibility for configuring storage systems based on specific requirements. Choose the RAID levels that best meet your needs, whether it’s a balance of performance and redundancy or prioritizing one over the other.
Cost-Effective: Despite the need for extra disks, Nested RAID configurations offer cost advantages in system efficiency and data protection. It is crucial when considering expenses related to data recovery and system downtime due to disk failures.
Nested RAID: Choosing the Right Level
Choosing the right Nested RAID level is crucial for optimal performance and data protection. Each level has its characteristics that align with different operational requirements. The “best” Nested RAID varies based on specific organizational needs.
- RAID 10: RAID 10 combines speed and redundancy, making it ideal for demanding environments like databases and online transaction processing systems. Its main advantage is tolerating multiple drive failures without data loss, as long as they don’t occur in the same mirrored set.
- RAID 50: RAID 50 combines the benefits of RAID 5 and RAID 0, providing high data read rates and fault tolerance. It is suitable for multi-user environments prioritizing data storage overwrite performance.
- RAID 60: RAID 60 combines the advantages of RAID 6 and RAID 0, offering exceptional fault tolerance to withstand multiple drive failures. It is well-suited for high-performance systems and data availability and is ideal for file and email servers.
Before deciding, it is crucial to evaluate your data storage requirements and seek expert advice carefully. This will guarantee you choose the most efficient and dependable nested RAID level that suits your organization’s needs. By configuring it correctly, nested RAID has the potential to significantly enhance the performance and reliability of your data storage system, creating a strong basis for your organization’s operations.
Examples of Nested RAID Levels
Numerous industries widely use nested RAID setups for their exceptional performance and robust data protection capabilities. They cater to the specific needs of sectors like healthcare, finance, entertainment, and education. The following section will explore practical examples of various nested RAID levels, showcasing their adaptability and effectiveness in managing diverse data.
RAID 01 (0+1)
This configuration is similar to RAID 10 but reverses the sequence of operations.RAID 01 mirrors the data to provide redundancy and then strips these mirrored sets to improve performance. However, if more than one drive fails, data can be lost, making RAID 10 a more reliable option.
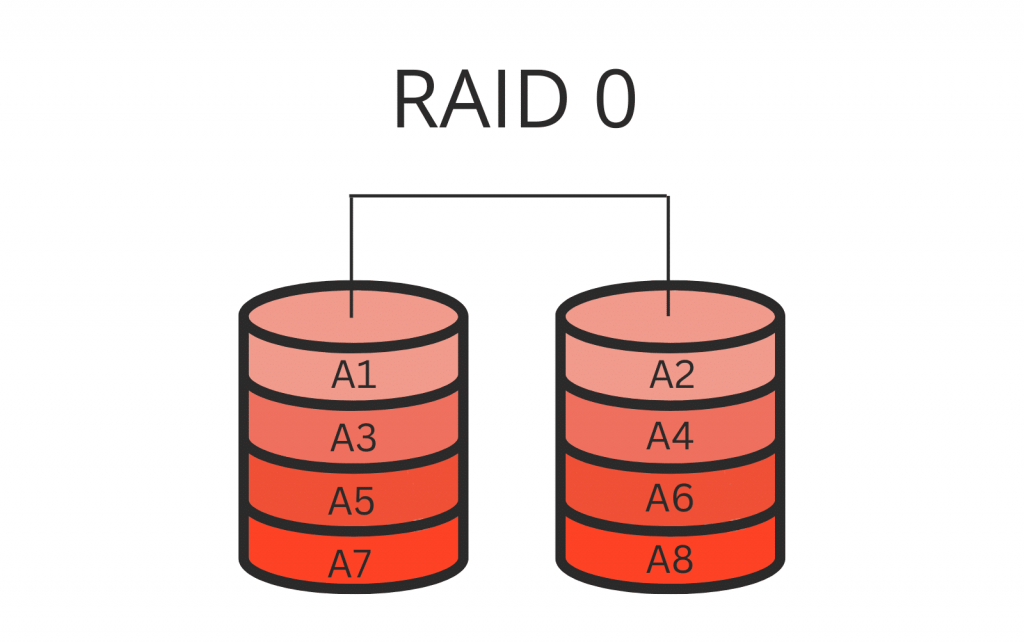
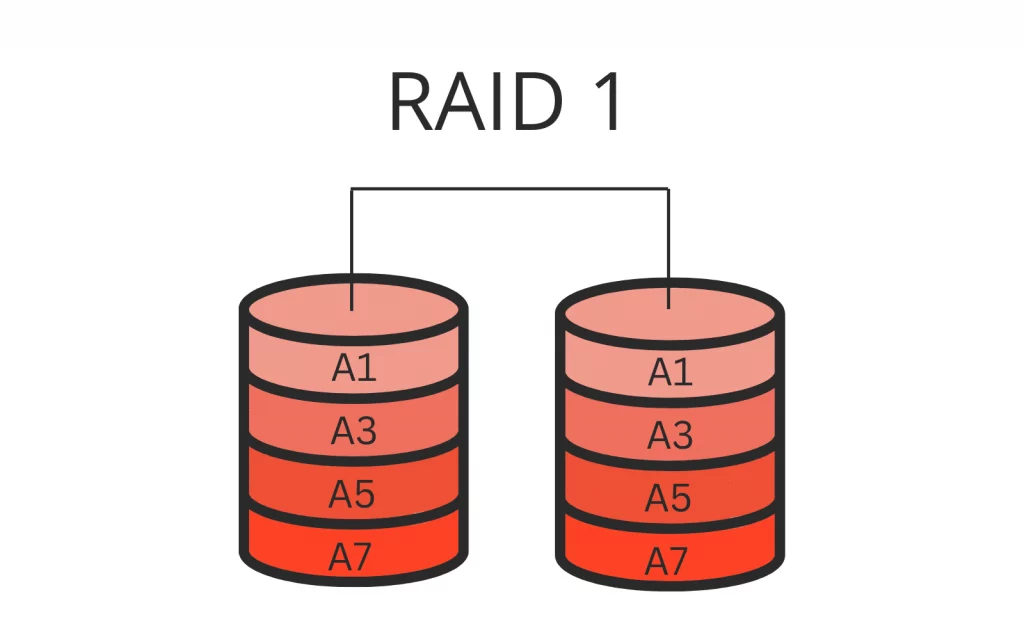
RAID 10 (1+0)
This level combines the striping feature of RAID 0 and the mirroring feature of RAID 1. In RAID 10, data is striped across several disks for increased speed and then mirrored to duplicate the data for redundancy. This highly efficient and reliable level provides strong protection against disk failures.
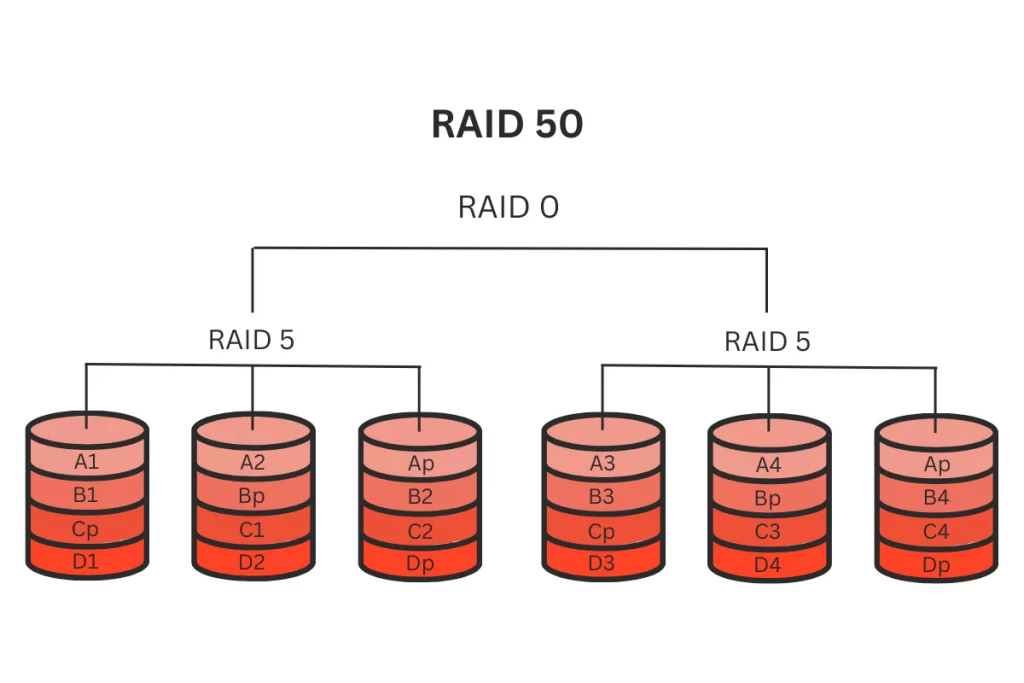
RAID 50 (5+0)
RAID 50 combines RAID 5 and 0. It uses striping like RAID 0 for improved performance and parity information like RAID 5 for redundancy. RAID 50 is beneficial for systems that require a balance between high data transfer rates and data redundancy.
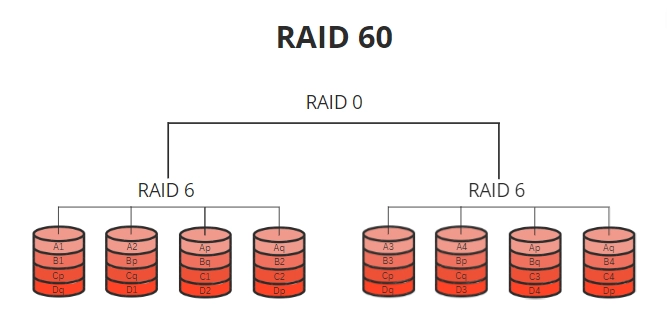
RAID 60 (6+0)
This is a combination of RAID 6 and RAID 0. RAID 60 uses striping for improved performance, with dual parity for redundancy, allowing for up to two drive failures within each RAID 6 array. This level is ideal for systems that require high data availability and can withstand multiple simultaneous drive failures without data loss.
RAID 100 (10+0)
This level blends the finest attributes of RAID 0 and RAID 1, employing striping and mirroring to amplify performance and fortify fault tolerance. Like RAID 10, it necessitates many disks, yet it is ideal for applications demanding exceptional data transfer rates and stringent fault tolerance prerequisites.


Drawbacks of Hybrid RAID
While Hybrid RAID configurations provide advantages such as improved performance, redundancy, and storage efficiency, it is crucial to acknowledge the associated limitations.
- Complexity: Setting up and managing hybrid RAID configurations, particularly nested ones, can present greater complexity. It demands a deep understanding of various RAID levels, which raises the risk of misconfiguration and potential data loss.
- Cost: Deploying multiple RAID levels often requires additional hard drives, escalating costs. Moreover, it necessitates acquiring advanced hardware or software components, further augmenting expenses.
- Recovery Difficulty: Data recovery can pose greater challenges regarding hybrid RAID systems in case of failures. Accurate data restoration requires specialized expertise and tools to navigate the complexity involved.

- Performance Variations: Performance levels may vary depending on the hybrid RAID configuration. For instance, some setups may offer superior read performance while sacrificing write speed due to parity calculations.
- Storage Efficiency: Mirroring in hybrid RAID configurations can considerably reduce storage capacity, as it allocates a significant portion of the total space for redundancy.
Hybrid RAID configurations offer a powerful combination of performance, storage efficiency, and data protection. However, it’s important to consider the complexity, cost, and data recovery challenges. In case of any data loss accidents, consider contacting PITS Global Data Recovery Services for reliable support and solutions. Our team of skilled experts excels in managing intricate data recovery situations, encompassing diverse RAID configurations, including hybrid RAID. We provide comprehensive solutions customized to your requirements, guaranteeing your invaluable data’s secure and efficient retrieval.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nested RAID?
Nested RAID, or hybrid RAID, is a collection of multiple nested levels, combining the features of different standard levels. It offers enhanced performance, data redundancy, and storage efficiency compared to single-level RAID configurations.
What is the difference between RAID and Nested RAID?
RAID refers to single-level configurations that offer data protection or improved performance by utilizing striping, mirroring, or parity information across multiple disks. On the other hand, nested RAID combines two or more standard levels to provide enhanced features and benefits. It offers a more customizable and efficient approach to data storage compared to single-level RAID configurations.
Why is expert consultation important when setting up hybrid RAID configurations?
Expert consultation is crucial for setting up hybrid RAID configurations. It requires a deep understanding of RAID levels, compatibility, and the organization’s needs. It minimizes the risk of misconfiguration, data loss, and other complications. Expert support ensures accurate and efficient data recovery in case of issues or data loss.
What is RAID 100, and when is it used?
RAID 100, also known as RAID 1+0+0, is a nested RAID level that combines features of RAID 0 and RAID 1 arrays. It provides high performance, data redundancy, and storage efficiency, making it ideal for large enterprises with critical storage and performance needs. However, managing and deploying RAID 100 can be complex and expensive compared to other nested RAID levels.
Is Nested RAID suitable for all types of data storage?
Nested RAID is suitable for different types of data storage, but its effectiveness relies on factors like data type, volume, and performance requirements. For example, it may be better for highly transactional databases that demand constant read-and-write operations. Carefully evaluate your data storage needs before implementing any RAID configuration.
