SATA, IDE, and AHCI are three interfaces that link storage devices to a computer’s motherboard, like hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs). These interfaces govern the data exchange between the storage device and the computer. SATA, IDE, and AHCI are widely used storage interfaces that enable efficient data transfer and storage.
What is SATA
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment is a contemporary computer bus interface that links host bus adapters to storage devices, for example, hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. SATA has replaced the older Parallel ATA (PATA) and presents numerous advantages. These include faster data transfer rates, slimmer and more flexible cables promoting improved airflow within computer cases, and the convenience of hot-swapping devices.
Additionally, SATA drives are renowned for their ease of installation and configuration, making them a popular choice for personal and commercial computing systems.
They provide faster data transfer rates, significantly enhancing overall system performance and efficiency. The thinner and more flexible design of SATA cables promotes superior airflow within the system, reducing the risk of overheating.

Despite their benefits, Their interfaces do have a few limitations. Firstly, it does not support multiple drives on the same cable; each drive requires its dedicated cable. It can result in cable clutter in larger systems. While SATA is faster than its predecessor, PATA, it still needs to improve compared to newer interfaces like NVMe. NVMe and SATA are different interfaces for connecting storage devices to a computer.
What is IDE
IDE, which stands for Integrated Drive Electronics, was once utilized as an interface to link storage devices, including hard drives and optical drives, to a computer’s motherboard. Unlike previous systems where the controller was part of the motherboard, IDE integrated the controller directly into the hard drive.
This innovation resulted in a significant boost in data transfer rates during its introduction. Even though SATA and other interfaces have mostly replaced IDE (Parallel ATA or PATA) in modern computers, older systems still utilize IDE due to its compatibility with a wide range of drives and cost-effectiveness.

IDE drives provided several advantages during their prominence as the primary storage interface in computers. Additionally, IDE ensured backward compatibility with older PATA devices and controllers. Lastly, the straightforward installation process of IDE made it accessible to users with diverse technical expertise.Despite the advantages of IDE, it eventually became outdated and was replaced due to several limitations.
IDE’s main drawback was its sluggish data transfer rates, negatively affecting system performance. Moreover, compatibility issues with newer operating systems and devices became apparent as IDE became outdated.
What is AHCI mode
Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) is a technical standard defined by Intel that specifies the operation of SATA host bus adapters. Introduced as a successor to IDE, AHCI offers several advantages over the older interface, making it a crucial component in modern computing systems. AHCI allows software to communicate with (SATA) devices to deliver functionalities that aren’t possible with IDE, such as hot-swapping and native command queuing. This mode enhances hard drive performance and enables the system to run more smoothly.
While AHCI is more sophisticated than the older IDE, it does require appropriate drivers to function correctly, which can complicate the installation process. However, it’s important to note that most modern operating systems, including Windows and Linux distributions, come with built-in support for AHCI, simplifying the setup. Overall, AHCI stands as a powerful interface that boosts the capabilities of SATA devices, significantly enhancing data transfer rates and storage performance in contemporary computer systems.
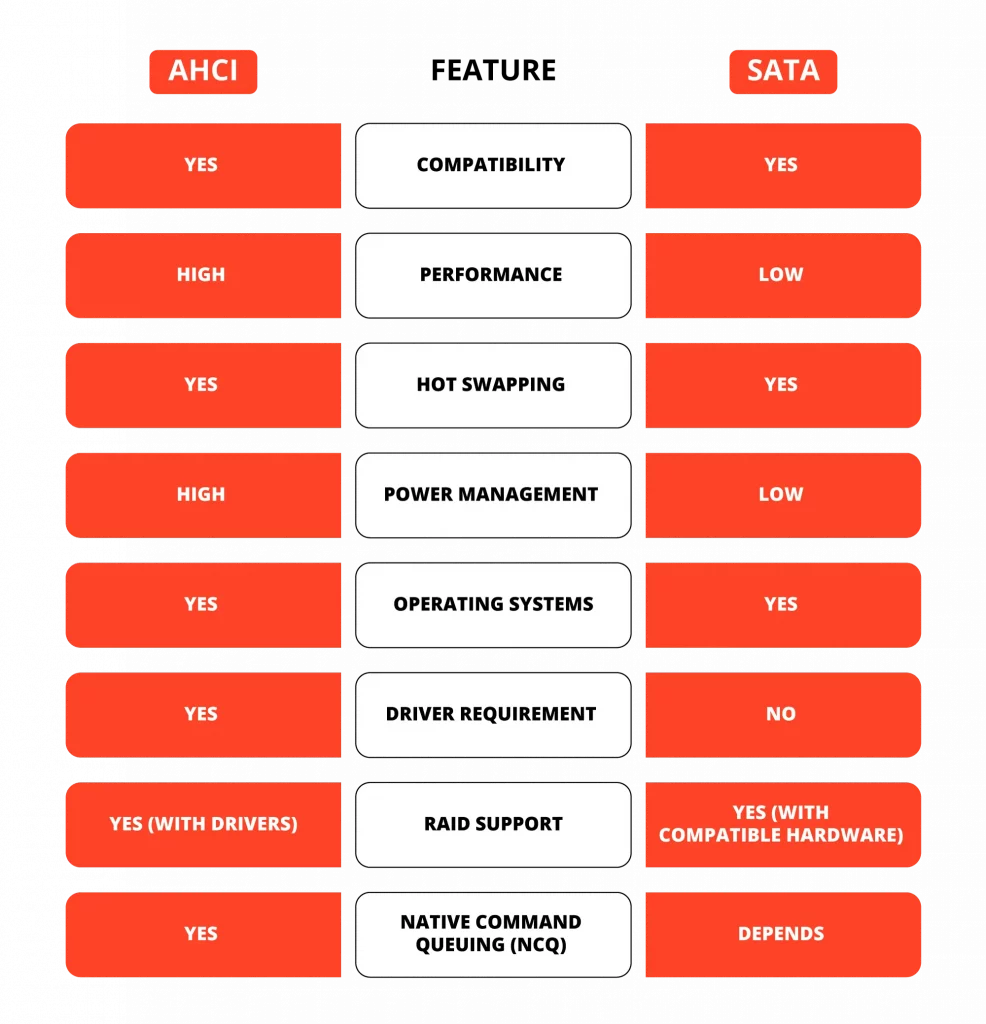
AHCI vs SATA
While discussing SATA vs AHCI, it is important to note that they serve different purposes and functions on different layers within a computer system. SATA is a hardware interface that links hard drives and SSDs to the computer’s motherboard.
On the other hand, AHCI, or Advanced Host Controller Interface, is a software protocol that defines the operation of SATA interfaces. It optimizes its functionality by taking advantage of features inherent to SATA, such as Native Command Queuing and hot swapping. AHCI improves communication between the SATA hardware and the system, enhancing performance and more efficient data management. In essence, SATA serves as the physical pathway for data, while AHCI transfers that data.
They work together to allow your computer to interact effectively with storage devices. SATA establishes the physical connection required for data transfer, while AHCI facilitates data transfer, optimizing SATA’s functionality.
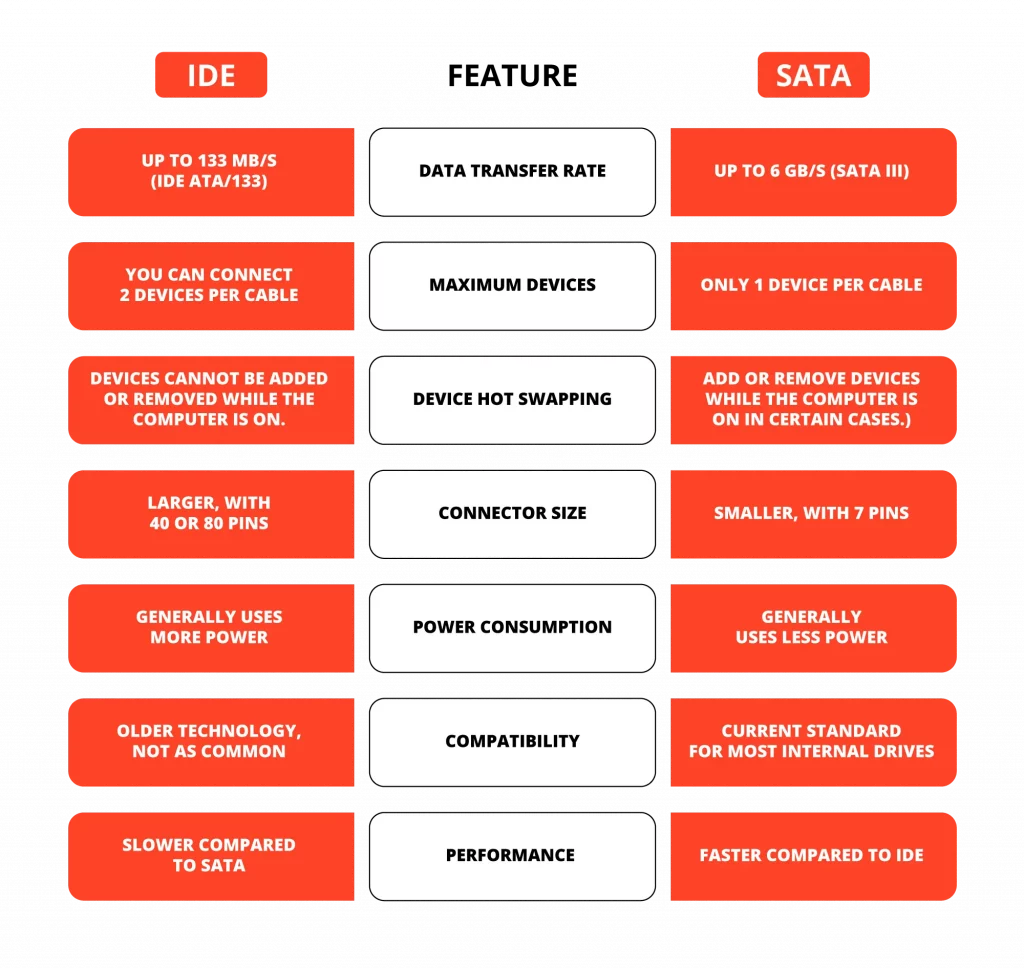
IDE vs AHCI
IDE vs AHCI: When comparing, the primary distinction between the two lies in functionality and performance. AHCI, specifically designed for SATA drives, fully utilizes their capabilities, including hot-swapping and Native Command Queuing (NCQ), which are unsupported by IDE. Additionally, AHCI offers enhanced data transfer rates, improving system performance and efficiency. Furthermore, AHCI automatically detects and configures new drives, providing a seamless experience for users.

The most notable are slower data transfer rates and a need for more support for advanced features like hot-swapping and NCQ. IDE does not automatically recognize and configure new drives, necessitating manual user configuration. However, one advantage of IDE is its compatibility with a wider range of drives, including older PATA devices.
Despite this, IDE’s limitations have led to its replacement with more advanced interfaces in modern computer systems. The superior swiftness, adaptability, and effectiveness provided by these more recent technologies have established AHCI as the preferred option for enhancing system performance and efficiently managing data.
Performance Comparison: IDE vs AHCI
Performance is a key factor when evaluating IDE vs AHCI. AHCI, a valuable technological advancement, offers more significant performance benefits than IDE mode. By enabling AHCI mode, your computer can fully leverage the advantages of SATA, including faster data exchange with HDD and SSD through NCQ technology. It leads to improved file access speed and overall computer performance. Enabling AHCI mode can greatly enhance your computer’s efficiency in accessing files on storage devices.
IDE vs SATA: Which is the Best Choice
When comparing SATA drive vs IDE, it becomes evident that SATA is the preferred choice for modern computer systems. The advancements and performance of SATA vs AHCI make it the optimal option for efficient data management. While IDE may have certain advantages, its limitations are becoming more apparent with the rapid development of computing technology.
Although there may be situations where IDE remains viable, AHCI vs SATA has become the standard for contemporary computing systems. With their improved performance, compatibility with newer technologies, and efficient data management capabilities, SATA and AHCI surpass IDE in optimizing system performance and safeguarding valuable data. Therefore, when considering IDE vs SATA, it is evident that SATA is the superior choice in nearly all aspects. It offers enhanced speed, compatibility, and advanced features, making it an indispensable component of modern computing systems.
In conclusion, when choosing between AHCI, SATA, and IDE, recent technological advancements have positioned AHCI and SATA as the superior options for most modern computing requirements. AHCI offers efficient data management, while SATA provides high-speed data transfer rates. Both choices are compatible with new technologies, surpassing the aging IDE interface. However, it is important to consider the unfortunate risk of data loss in any storage technology. In such a circumstance, please don’t hesitate to contact our team at PITS Global Data Recovery. With extensive experience in data recovery and the necessary expertise and tools, we are dedicated to retrieving your valuable data, ensuring uninterrupted operations and minimal disruption.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use the IDE hard drive with SATA?
A converter or adapter can connect an IDE hard drive to a SATA interface. However, it is crucial to note that this may result in diminished performance compared to using a native SATA drive. Thus, verifying motherboard and BIOS compatibility is essential before implementing any modifications. Generally, upgrading to a SATA interface is advisable to enhance overall system efficiency.
Why is SATA faster than PATA?
SATA outperforms PATA in speed thanks to its serial data transfer method, which transmits data one bit at a time instead of in parallel like PATA. It leads to quicker data transfer rates and improved overall system performance.
Should SSD use AHCI or IDE?
SSDs should use AHCI rather than IDE. AHCI allows the use of advanced features, such as Native Command Queuing (NCQ), which can significantly enhance the performance of SSDs. IDE, on the other hand, is an older interface that needs to have these advanced features, potentially limiting the performance of an SSD. Therefore, for optimal performance and to fully leverage the capabilities of SSDs, it is recommended to use AHCI.
Why are SATA and AHCI considered superior to IDE?
SATA and AHCI are considered superior options for performance, compatibility with modern technologies, and efficient data management features. Additionally, they provide greater flexibility in system design and contribute to improved internal airflow.
What are some strategies to prevent data loss with AHCI and SATA?
To prevent data loss, you can employ multiple strategies. These encompass setting up RAID configurations to ensure data redundancy and using software-based backup solutions to create additional copies of data. Maintaining consistent data protection can be accomplished by scheduling regular backups.
